Breadcrumb
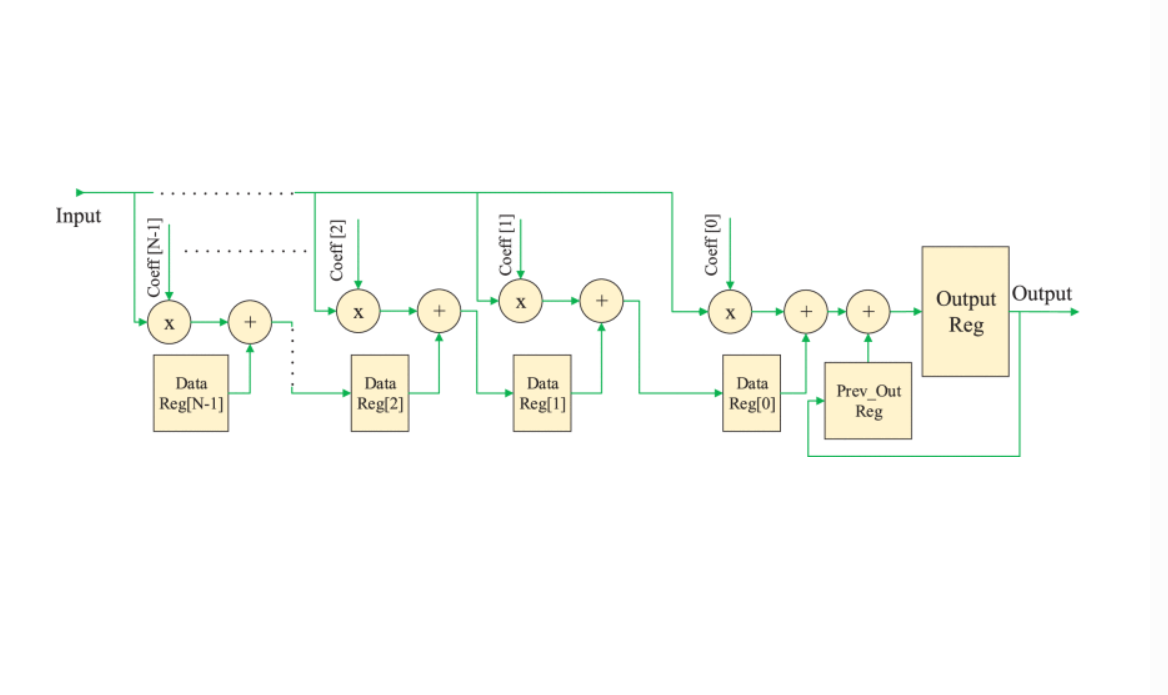
Hardware Accelerator of Fractional-Order Operator Based on Phase Optimized Filters With Applications
Hardware accelerators outperform CPUs in terms of performance by parallelizing the algorithm architecture and using the device’s programmable resources. FPGA is a type of hardware accelerator that excels not only in performance but also in energy efficiency. So, it provides a suitable platform for implementing complicated fractional-order systems. This paper proposes a novel phase-based optimization method to implement fractional operators using FIR and IIR filters. We also compare five fractional operator implementation methods on FPGA regarding resource utilization, execution time, power

Double Visual Cryptography Using Generalized Tent Map, Rotation, and Image Filtering
This paper introduces a Multi-Visual Cryptography (MVC) system for sharing two color images, where the secrets can be revealed with low computation power using all the shares. The system uses the generalized Tent map as a source of randomness to generate any number of random shares. More specifically, (n-1) random shares are generated, and then, the nth share is calculated from the random shares and the secrets using rotations of the shares. In recovery, rotation of the last share recovers the two images based on the angle of rotation. Half the number of pixels is recovered for each secret

Battery Modeling with Mittag-Leffler Function
In various areas of life, rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are the technology of choice. Equivalent circuit models are utilized extensively in characterizing and modeling energy storage systems. In real-time applications, several generic-based battery models are created to simulate the battery's charging and discharging behavior more accurately. In this work, we present two generic battery models based on Mittag-Leffler function using a generic Standard battery model as a reference. These models are intended to fit the continuous discharging cycles of lithium-ion, Nickel-cadmium, and Nickel
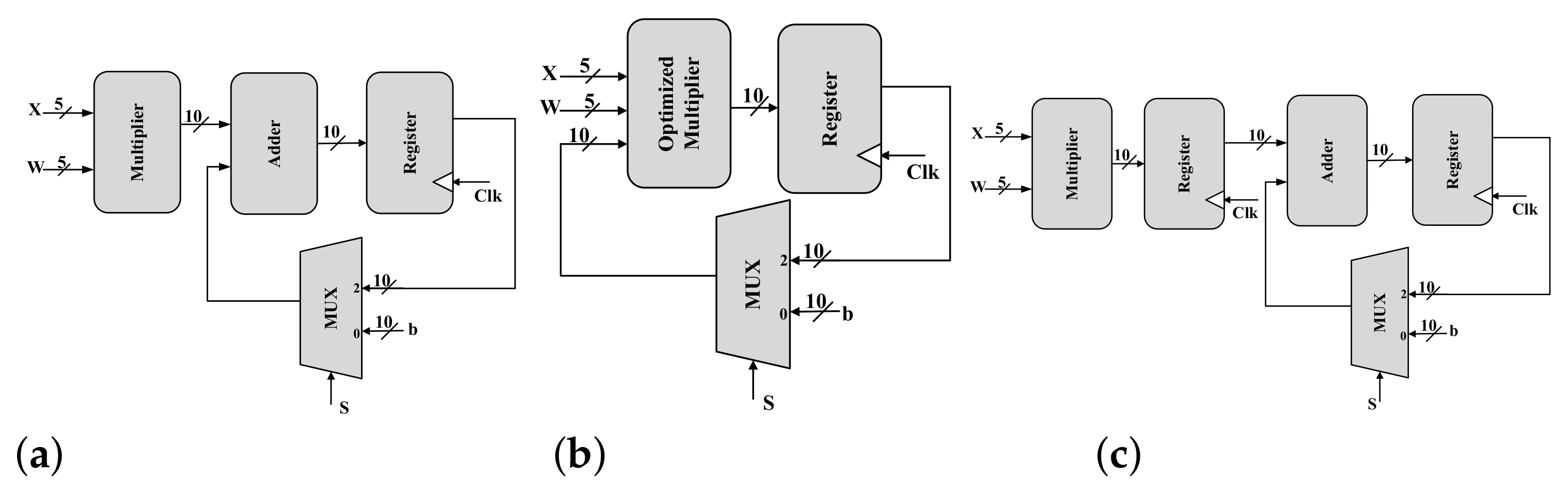
CNTFET-Based Ternary Multiply-and-Accumulate Unit
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) is one of the most commonly used operations in modern computing systems due to its use in matrix multiplication, signal processing, and in new applications such as machine learning and deep neural networks. Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. In this paper, a MAC is proposed using a CNTFET-based ternary logic number. Specifically, we build a 5-trit multiplier and 10-trit adder as building blocks of two ternary MAC unit designs. The first is a basic MAC which has two methods to
A Study on Fractional Power-Law Applications and Approximations
The frequency response of the fractional-order power-law filter can be approximated by different techniques, which eventually affect the expected performance. Fractional-order control systems introduce many benefits for applications like compensators to achieve robust frequency and additional degrees of freedom in the tuning process. This paper is a comparative study of five of these approximation techniques. The comparison focuses on their magnitude error, phase error, and implementation complexity. The techniques under study are the Carlson, continued fraction expansion (CFE), Padé, Charef
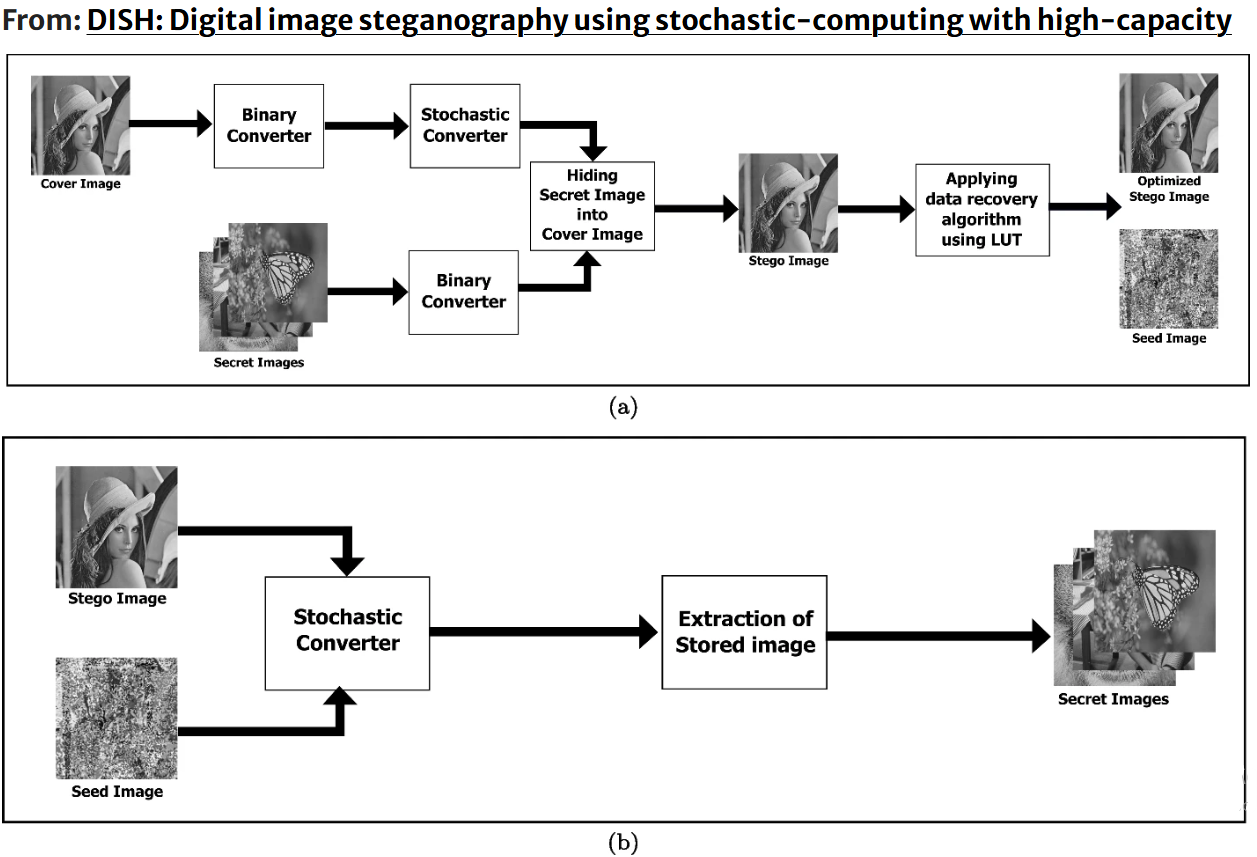
DISH: Digital image steganography using stochastic-computing with high-capacity
Stochastic computing is a relatively new approach to computing that has gained interest in recent years due to its potential for low-power and high-noise environments. It is a method of computing that uses probability to represent and manipulate data, therefore it has applications in areas such as signal processing, machine learning, and cryptography. Stochastic steganography involves hiding a message within a cover image using a statistical model. Unlike traditional steganography techniques that use deterministic algorithms to embed the message, stochastic steganography uses a probabilistic

Enhancing the Performance of Thin Film Photovoltaic Solar Cells using Truncated Conical Nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics are considered as promising photovoltaic candidate with enhanced optical absorption and quantum efficiency by embedding metallic nanoparticles in the photovoltaic active layer. In this paper, the efficiency enhancement of ultra-thin film solar cells with embedded truncated cone nanoparticles is studied. First, the natural electric field modes of the truncated cone in free-space are examined when excited by a plane wave. Parametric study is then performed to investigate the effects of the geometrical parameters of the structure on its resonant modes. Second, a uniform

Bowtie-Shaped Plasmonic Nanoparticles-Enhanced Photovoltaic Anti-Reflective Coating
Light trapping is a promising technique that enhances sunlight absorption by solar cells. This paper presents a study of bow-tie-shaped nanoparticles embedded in the antireflection coating of photovoltaic solar cells, which enhances the optical transmission of the photovoltaic surface. Therefore, the optical path length for light penetration is increased through the semiconductor active layer. First, the fundamental electric field modes of a single nanoscaled bow-tie are examined under excitation of plane waves with different polarizations. Second, an array of bow-tie-shaped nanoparticles is

Capacitive Power Transfer Modeling of Charging Inner-body Devices
Wireless power transfer (WPT) is highly desirable for applications with battery restrictions, such as biomedical applications. For example, in the case of implantable devices, power is transmitted through the human body, which has dielectric characteristics that must be considered during the design of the WPT system. This paper examines capacitive power transfer through the human body and formulates the complete WPT system, including the human body model. The power delivered to the implantable device is also analyzed. Finally, the system efficiency is discussed under different body and load
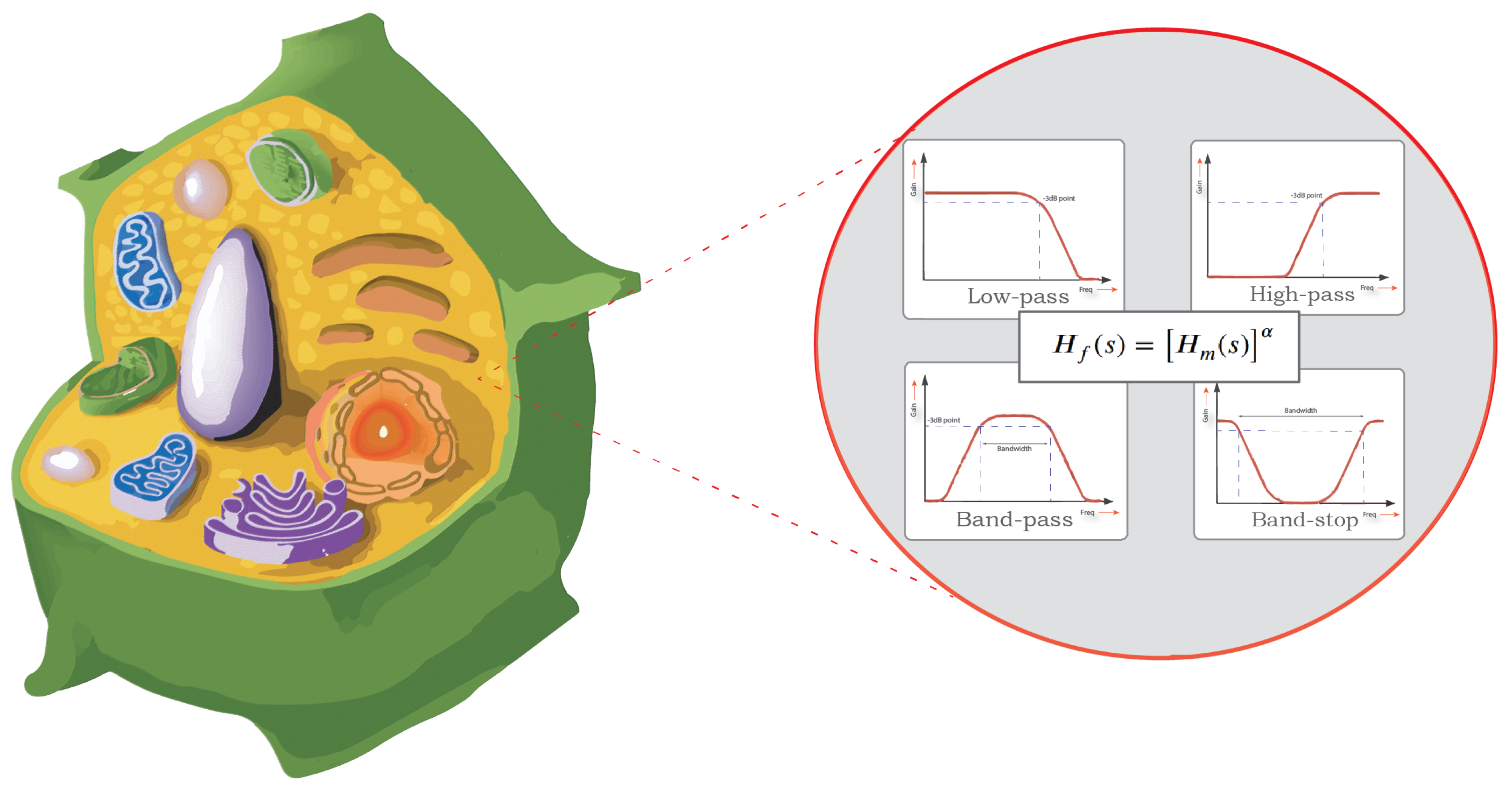
Plant Tissue Modelling Using Power-Law Filters
Impedance spectroscopy has became an essential non-invasive tool for quality assessment measurements of the biochemical and biophysical changes in plant tissues. The electrical behaviour of biological tissues can be captured by fitting its bio-impedance data to a suitable circuit model. This paper investigates the use of power-law filters in circuit modelling of bio-impedance. The proposed models are fitted to experimental data obtained from eight different fruit types using a meta-heuristic optimization method (the Water Cycle Algorithm (WCA)). Impedance measurements are obtained using a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
