Research Project
Research Project
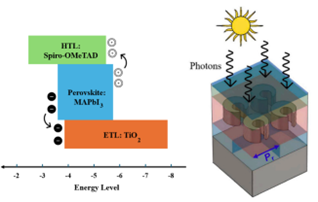
Optical Nano-antennas for Photovoltaic and Infra-red Sensing Applications
Objectives: The main objectives of the project are listed below: Developing new plasmonic nano structures along with proposing new array topologies by considering uniform distribution, 2D or 3D linear and gaussian distributions. Also, the proposed work aims at investigating the passivation effect of the nanoparticles by surrounding it with a thin layer of silica. Testing different metaheuristics
Research Project
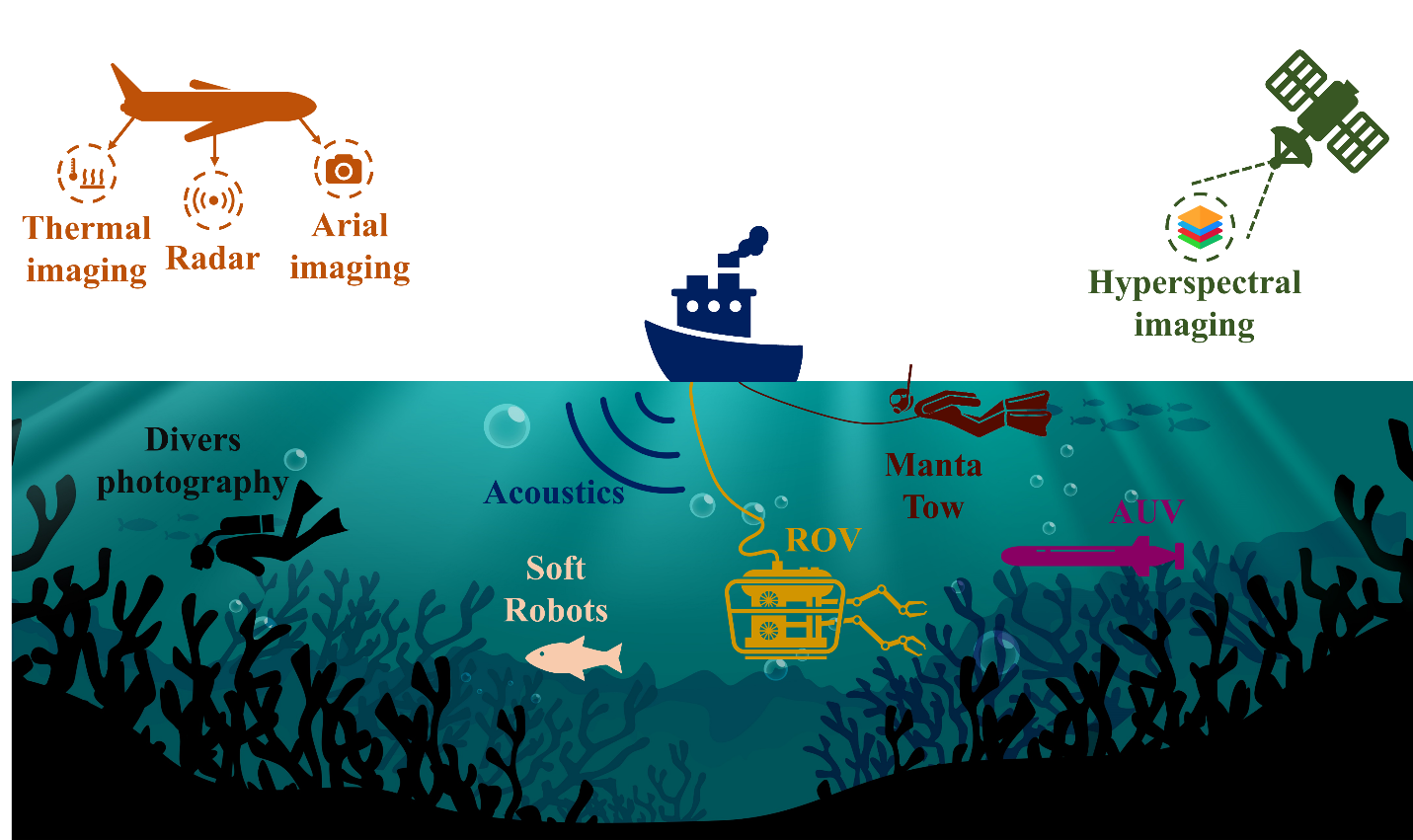
Bio-inspired Soft Robot for Monitoring Coral Reefs
Abstract Coral reefs play a crucial role in supporting a quarter of all aquatic life, but their existence is now threatened by ongoing climate changes. Our project aims to develop an underwater soft robot that can mimic the morphology and shape of actual marine creatures and to imitate their swimming motion. This robot can play a critical role as monitoring platform to understand the reefs

Research Project
Bio-Mimetic Locomotion of Soft Turtle Robot
Abstract Amphibious robots have great potential for a variety of applications, but their design can be complex and expensive. Bio-inspired soft robotics offers a promising solution, as their actuators can perform evenly on land and underwater. Our robot takes inspiration from turtle locomotion as it bridges the gap between traditional four-legged robots and swimming robots. The robot can be

Research Project
Terahertz Metamaterial Structures for Biomedical Sensing Applications
A new design of interdigitated E-shaped metamaterial sensor has been proposed. The structure has been intensively studied using CST software and is optimized to achieve ultrahigh sensitivity at the Terahertz range. Two different structures of the E-shaped sensors have been proposed. Both structures are characterized by a high absorption level at their resonant peaks with an ultra-high sensitivity

Research Project
Improving Job Market Skills of Graduates
In Egypt and its neighbouring countries, a mismatch between educational output and training requirements of the labour market has been a significant constraint on economic development. Pre-employment skills are essential to prepare newly graduated students for the job market in the industry as well as academia. AGYA members Dr. Lobna Said, Dr. Mohamed Abou El-Enein, Dr. Shadi Albarqouni and Dr

Research Project
Making Graduates in Egypt, Libya and Palestine Ready for the Job Market
Objectives/Contributions: Many Arab countries have to deal with discrepancies between the educational output and the actual needs of their labour markets. Introducing capacity-building trainings for new graduates is an optimal approach to bridge this gap, improve their skills and increase their marketability for industry or academia, which is the aim of the project by the AGYA Working Group Arab
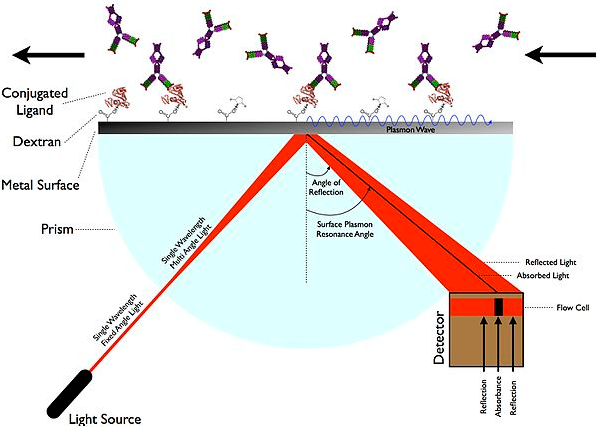
Research Project
Plasmonic Sensors for Biomedical and Infra-Red Detection Application
Objective/Contributions: The project aims at proposing a new Infra-Red sensor design by employing a plasmonic effect. Plasmonic devices have great potential for biomedical applications due to the sensitivity of the localized surface plasmon resonance to the surrounding medium. Therefore, proposed metasurface sensors are tuned for Biomedical applications as medical diagnostic tools. Enhancing

Research Project
Multi-purposes Reading IoT-based Smart Platform
Objectives/Contributions: The project aims to introduce a solution for a multi-protocol environment. The proposed device that represents the ultimate goal of the project will act as an interpreter between different communication media, representing the project’s main deliverable. Furthermore, we propose to have a smart device to estimate the channel performance and decide the optimum communication
Research Project
Low-Power Artificial Intelligence Framework for Internet of Things Applications
The Internet of Things (IoT) is penetrating many facets of our daily life with the proliferation of intelligent services and applications empowered by artificial intelligence (AI). Due to the massive scalability of modern IoT networks and increased data privacy, traditional AI algorithms require centralized data collecting and processing, which may not be practical in real-world application
