Breadcrumb

Semi-Fragile Watermark for the Authentication and Recovery of Tampered Images
In order to strengthen the safety of corporate multimedia assets, a semi-fragile watermarking method is developed, which makes use of the integer wavelet transform (IWT) and the discrete cosine transform (DCT) for tamper detection and recovery. In this paper, we produce two distinct kinds of watermarks: an authentication watermark and a recovery watermark. A tamper detection methodology is utilized at the receiving end to check the watermarked image for validity and detect any assaults. If the changes are determined to be malicious, the suggested tamper recovery method is used to restore the

Modified Arnold Transform and DNA Manipulation for Chaos-Based RGB Image Encryption
Multimedia applications use image encryption algorithms extensively to safeguard and authenticate digital images. This paper presents an RGB image encryption method, which uses Chaos, DNA, pixel sum, and modified Arnold transform. The suggested algorithm is validated to be robust and resistant to visual, statistical, differential, and brute-force attacks. Additionally, the resulting encrypted images pass all tests of the NIST SP 800-22 test suite. © 2023 IEEE.
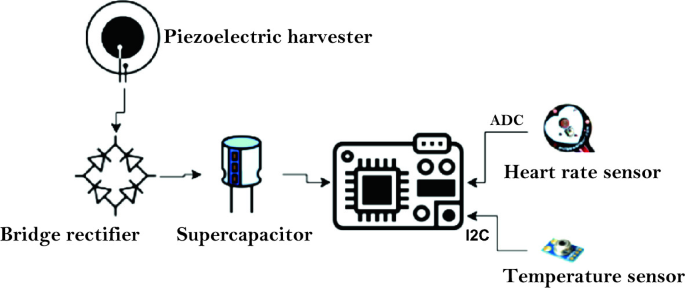
Energy Aware Tikhonov-Regularized FPA Technique for Task Scheduling in Wearable Biomedical Devices
Harvesting the energy from environmental sources is a promising solution for perpetual and continuous operation of biomedical wearable devices. Although the energy harvesting technology ensures the availability of energy source, yet power management is crucial to ensure prolonged and stable operation under a stringent power budget. Thus, power-aware task scheduling can play a key role in minimizing energy consumption to improve system durability while maintaining device functionality. This chapter proposes a novel biosensor task scheduling of energy harvesting-based biomedical wearable devices
Realistic Wireless Smart-Meter Network Optimization Using Composite RPL Metric
In smart metering applications, transferring and collecting data within delay constraints is crucial. IoT devices are usually resource-constrained and need reliable and energy-efficient routing protocol. Furthermore, meters deployed in lossy networks often lead to packet loss and congestion. In smart grid communication, low latency and low energy consumption are usually the main system targets. Considering these constraints, we propose an enhancement in RPL to ensure link reliability as well as low latency. We refer to the proposed new additive composite metric as Delay-Aware RPL (DA-RPL)
A Lightweight Image Encryption Scheme Using DNA Coding and Chaos
Protecting transmitted multimedia data such as images is a significant concern. This work proposes an encryption algorithm for greyscale images using a Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG), DNA coding, and pixel sum. The proposed approach is implemented on a Genesys 2 FPGA using minimal hardware resources and can operate at a maximum frequency of 110.8 MHz. In addition, several performance evaluation tests are conducted for multiple images, including statistical analysis of the encrypted image, keyspace analysis, and differential attack analysis. The system is compared to recent works with

Adsorption as an Emerging Technology and Its New Advances of Eco-Friendly Characteristics: Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analysis
Water contamination with paints causes a colour agent to the water that negatively affects the environment, organisms, and humans. Different physicochemical processes are applied for wastewater treatment; however, they have many drawbacks such as high cost, generating toxic waste, and non-effective at low concentrations. Adsorption is considered a promising technique for pollutant removal from polluted wastewater. Commercial activated carbon, nano-materials, and natural biological materials are used as adsorbents in adsorption. This chapter focuses on discussing the adsorption process, the

Sustainable Energy-Aware Task Scheduling for Wearable Medical Device Using Flower Pollination Algorithm
Power management and energy conservation are crucial for medical wearable devices that rely on energy harvesting. These devices operate under strict power budgets and require prolonged and stable operation. To achieve this, Energy-aware task scheduling is proposed as a solution to minimize energy consumption while ensuring the continued operational capabilities of the device. our paper presents a task scheduling method using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). The proposed task scheduling focuses on managing the activity of key components such as the heart rate sensor, temperature sensor
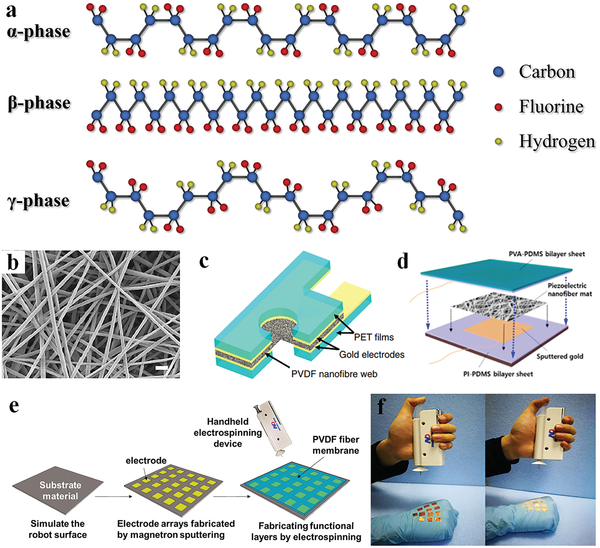
Improvement of piezoresistive pressure sensor using zig-zag shaped and PVDF material
Due to a wide range of applications in the biomedical industry, the need for flexible and wearable sensors is growing every day. A pressure sensor generates a signal based on the applied pressure. Sensors have become an integral component of our daily lives, from personal gadgets to industrial machinery. The identification of the low signal from the body necessitates the use of particularly sensitive sensors. The development of a pressure sensor that can transform the maximum input signal into an electrical output is critical. In this paper, zig-zag piezoresistors on a square diaphragm were
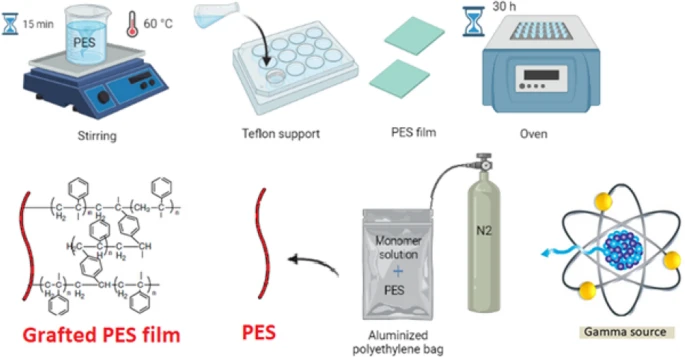
Effect of reaction conditions on gamma radiation-induced graft polymerization of α-methyl styrene onto polyethersulfone films: a kinetic study
In this work, gamma irradiation from a cobalt 60Co source was used to graft Copolymerize α-methyl styrene (AMS) onto Polyethersulfone (PES) films. Grafting reaction was performed at ambient temperature by simultaneous method applying different dose rates for a total absorbed dose of 30 kGy. The effects of reaction conditions including, dose rate, monomer concentration and absorbed dose on the grafting yield (DOG) were studied. Results showed that the grafting conditions influence considerably DOG. In addition, the depth understanding of the graft copolymerization reaction kinetics under
An Efficient DMO Task Scheduling Technique for Wearable Biomedical Devices
The popularity of wearable devices has grown as they improve the quality of life in many applications. In particular, for medical devices, energy harvesters are the dominating source of energy for wearable devices. However, their power budget is limited. Thus, power-saving techniques are essential components in the whole technology stack of those devices. That is, choosing the optimal schedule for different tasks running on the wearable device can help to reduce energy consumption. This paper presents a sensor task scheduling technique for optimizing energy consumption for energy harvesting
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
