Breadcrumb
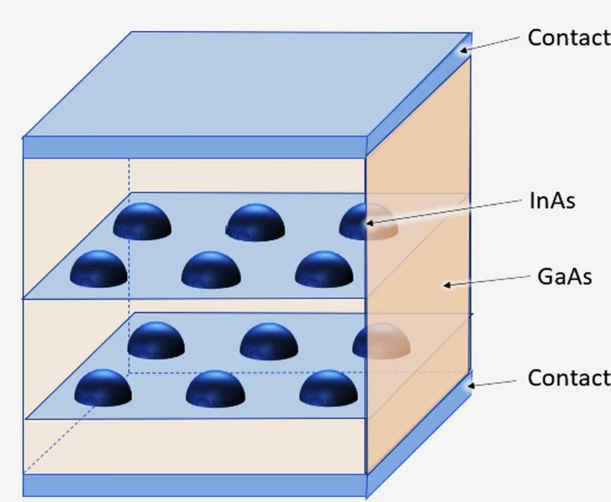
Modeling of dark current in semispherical quantum dot structures for infrared photodetection
Due to its tunable heterojunction bandgap and great sensitivity to normal incident illumination, the Quantum Dot Infrared Photodetectors (QDIPs) have received a lot of attention for the purpose of infrared sensing. It could be a very promising replacement for conventional infrared photodetectors made with established technology, including mercury cadmium telluride and quantum well infrared photodetectors. In this work, a model for the dark current in semispherical QDIP has been developed, resolves the primary semiconductor Poisson's and continuity equations, where the wave function and the
Small Area and Low Power Hybrid CMOS-Memristor Based FIFO for NoC
Area and power consumption are the main challenges in Network on Chip (NoC). Indeed, First Input First Output (FIFO) memory is the key element in NoC. Increasing the FIFO depth, produces an increas in the performance of NoC but at the cost of area and power consumption. This paper proposes a new hybrid CMOS-Memristor based FIFO architecture that consumes low power and has a small size compared to the conventional CMOS-based FIFOs. The predicted area is approximately equal to the half of that wasted in conventional FIFOs. The implementation of FIFO controller module is implemented using HDL

Novel Fast Prediction Algorithm for Advanced and High Efficiency Video Coding
This paper introduces an efficient prediction algorithm tailored for advanced and high efficiency video coding, encompassing both H.264 and H.265. The proposed approach aims at replacing the standard intra prediction methodology by employing a streamlined prediction mode, which significantly reduces computational overhead and system complexity while eliminating the requirement for mode decision. By leveraging block comparison criteria, the designed method combines neighboring blocks in a linear fashion to accurately represent the target block. Extensive comparisons are conducted with the H.264

Enhancement of plasmonic photovoltaics with pyramidal nanoparticles
Light trapping as a result of embedding plasmonic nanoparticles (NPs) into photovoltaics (PVs) has been recently used to achieve better optical performance compared to conventional PVs. This light trapping technique enhances the efficiency of PVs by confining incident light into hot-spot field regions around NPs, which have higher absorption, and thus more enhancement of the photocurrent. This research aims to study the impact of embedding metallic pyramidal-shaped NPs inside the PV’s active region to enhance the efficiency of plasmonic silicon PVs. The optical properties of pyramidal-shaped
Accelerated Edge Detection Algorithm for High-Speed Applications
Digital Image Processing (DIP) is a growing field for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles and video surveillance. To improve the performance of DIP systems, image processing algorithms are implemented in hardware rather than software. The idea here is primarily to get a faster system than software imaging or other alternative hardware. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have the advantages of parallel processing, low cost, and low power consumption. These semiconductor devices contain many logic blocks that can be programmed to perform everything from basic digital gate-level

Fractional order systems: An overview of mathematics, design, and applications for engineers
Fractional Order Systems: An Overview of Mathematics, Design, and Applications for Engineers introduces applications from a design perspective, helping readers plan and design their own applications. The book includes the different techniques employed to design fractional-order systems/devices comprehensively and straightforwardly. Furthermore, mathematics is available in the literature on how to solve fractional-order calculus for system applications. This book introduces the mathematics that has been employed explicitly for fractional-order systems. It will prove an excellent material for

Design Of Step Pyramidal Nanoparticle For Plasmonic Photovoltaics
Plasmonic Photovoltaics (PVs) are an effective method for increasing optical absorption by adding metallic nanoparticles to the photovoltaic active layer. The role of these nanoparticles is confining the incident light near them in the PV cell, resulting in thin film PVs of enhanced efficiency. Therefore, different materials and new NPs shapes are used for this purpose. In this research, a step pyramid is introduced as a novel structure for nanoparticles for enhancing plasmonic PVs by embedding an array of the proposed step pyramid nanoparticles within the PV cell. Therefore, the extinction
Biologically Inspired Optimization Algorithms for Fractional-Order Bioimpedance Models Parameters Extraction
This chapter introduces optimization algorithms for parameter extractions of three fractional-order circuits that model bioimpedance. The Cole-impedance model is investigated; it is considered one of the most commonly used models providing the best fit with the measured data. Two new models are introduced: the fractional Hayden model and the fractional-order double-shell model. Both models are the generalization of their integer-order counterpart. These fractional-order models provide an improved description of observed bioimpedance behavior. New metaheuristic optimization algorithms for

Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Overview on Protocols, Architectures, Technologies, Simulation Tools, and Future Directions
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a global network of interconnected computing, sensing, and networking devices that can exchange data and information via various network protocols. It can connect numerous smart devices thanks to recent advances in wired, wireless, and hybrid technologies. Lightweight IoT protocols can compensate for IoT devices with restricted hardware characteristics in terms of storage, Central Processing Unit (CPU), energy, etc. Hence, it is critical to identify the optimal communication protocol for system architects. This necessitates an evaluation of next-generation
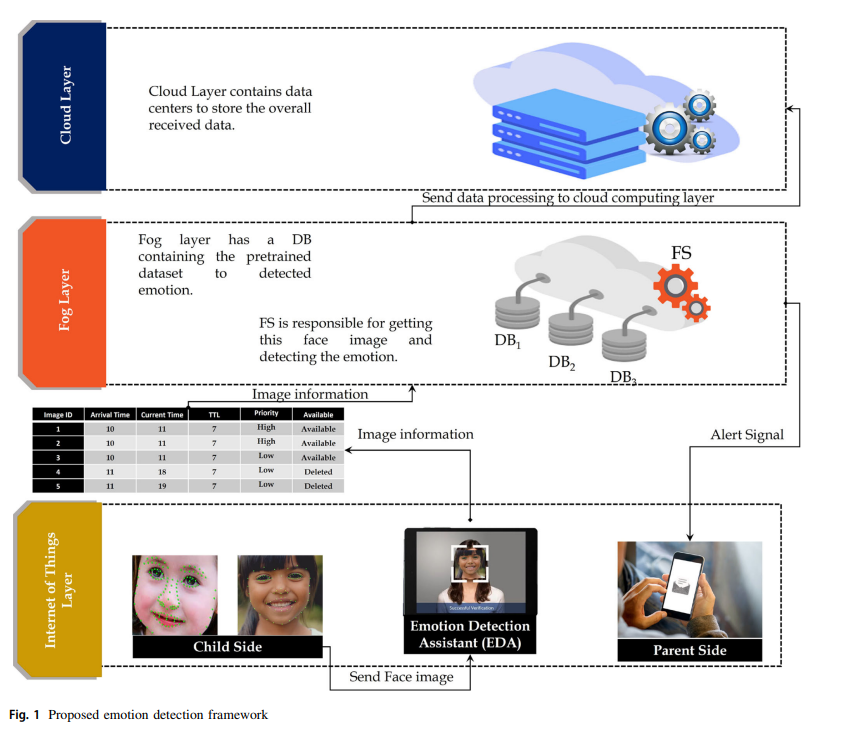
Real-time facial emotion recognition model based on kernel autoencoder and convolutional neural network for autism children
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is characterized by abnormalities in the brain, leading to difficulties in social interaction and communication, as well as learning and attention. Early diagnosis of ASD is challenging as it mainly relies on detecting abnormalities in brain function, which may not be evident in the early stages of the disorder. Facial expression analysis has shown promise as an alternative and efficient solution for early diagnosis of ASD, as children with ASD often exhibit distinctive patterns that differentiate them from typically
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
