Breadcrumb
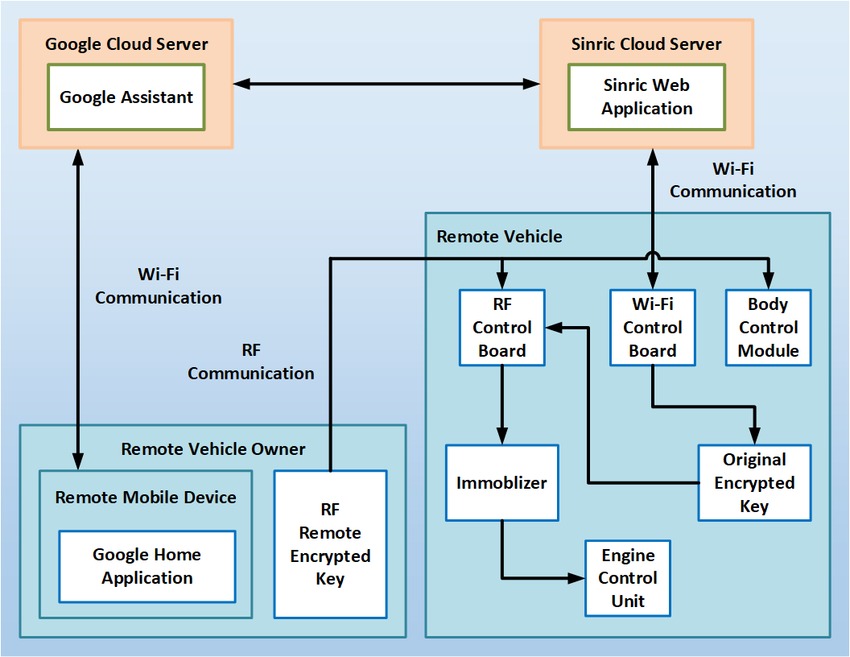
A Reliable Secure Architecture for Remote Wireless Controlling of Vehicle's Internal Systems based on Internet of Vehicles using RF and Wi-Fi
Internet of Vehicles is considered one of the most unprecedented outputs of the Internet of Things. No one has realized or even expected the rapidly-growing revolution regarding autonomous connected vehicles. Nowadays, Internet of Vehicles is massively progressing from Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks as a huge futuristic research and development discipline. This paper proposes a novel reliable and secure architecture for ubiquitously controlling remote connected cars' internal systems, such as engine, doors' locks, sunroof, horn, windows' and lights' control systems. The main contribution is that

Elementary Negative Group Delay Filter Functions
A theoretical study of the behavior of some elementary first- and second-order functions, which are suitable for realizing negative group delay, is performed in this work. As both the gain and phase responses are simultaneously considered, important derivations related to the actual bandwidth of operation are derived accompanied by useful design tips. The presented theory is supported by simulation and experimental results obtained through the utilization of typical active-RC filter structures, as well as from a field-programmable analog array device. © The Author(s) 2024.
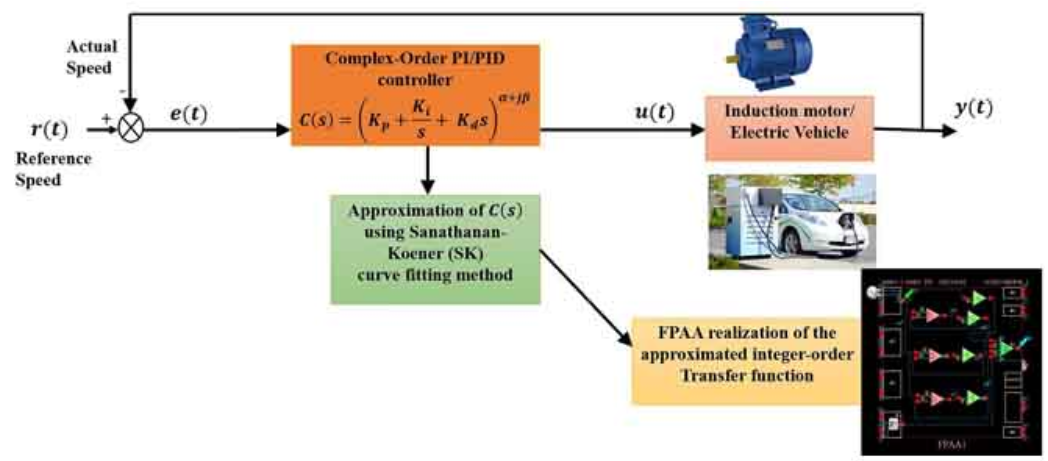
Design of Complex-Order PI/PID Speed Controllers and its FPAA Realization
Complex-order controllers are a generalized version of conventional integer-order controllers and are known to offer greater flexibility, better robustness, and improved system performance. This paper discusses the design of complex-order PI/PID controllers to control the speed of an induction motor drive and an electric vehicle. The speed-tracking performance of the complex-order controllers is compared with fractional-order controllers and conventional integer-order controllers. Implementing complex-order controllers is challenging due to commercial complex-order fractance element
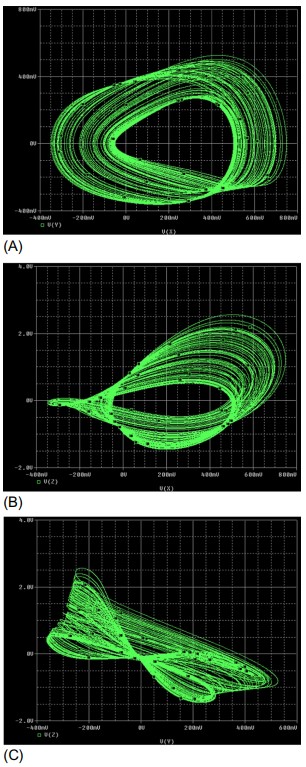
Dynamics, Circuit Design, Synchronization, and Fractional-Order Form of a No-Equilibrium Chaotic System
Systems without equilibrium such as electromechanical models with rotation and electrical circuits with cylindrical phase space were studied a long time ago. However, chaotic systems without equilibrium have received significant attention recently after the introduction of hidden attractors. Interestingly, an attractor of a no-equilibrium system is hidden because its basin of attraction does not intersect with any neighborhood of an unstable fixed point. This chapter presents a 3D no-equilibrium system with hidden chaotic attractors. The fundamental qualitative properties of the proposed no

Comment on “Origin of the Curie–von Schweidler law and the fractional capacitor from time-varying capacitance” [J. Pow. Sources 532 (2022) 231309]
In this Letter we highlight some fundamental errors in the paper “Origin of the Curie–von Schweidler law and the fractional capacitor from time-varying capacitance” [J. Pow. Sources 532 (2022) 231309] by V. Pandey. In particular, with the use of the convolution integral of linear time-varying capacitance with the time-derivative of voltage (i.e. Eq (9) as suggested by the author), one ends up with step voltage function generating a constant current on a capacitive device, which is not true. We also question that a step voltage results in zero charge according to the r.h.s. of Eq. (9), but in
Voltage-controlled M-M relaxation Oscillator
This paper discusses voltage-controlled M-M relaxation oscillator with analytical and circuit simulations. The introduced circuit has two different configurations based on the polarities of memristor; whether they are in the same direction or in the opposite direction. The Analytical formulas are function of the reference voltage such as the oscillation frequency and oscillation conditions for each case are derived with some numerical examples. The circuit simulations are introduced to validate the mathematical concepts as well as the effect of the reference voltage which can be used in
Bio-inspired adsorption sheets from waste material for anionic methyl orange dye removal
Abstract: Nano zero-valent iron (nZVI), bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0–Cu), and Raw algae (sargassum dentifolium) activated carbon-supported bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (AC-Fe0–Cu) are synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, XRD, and SEM. The maximum removal capacity is demonstrated by bimetallic activated carbon AC-Fe0–Cu, which is estimated at 946.5 mg/g capacity at the condition pH = 7, 30 min contact time under shaking at 120 rpm at ambient temperature, 200 ppm of M.O, and 1 g/l dose of raw algae-Fe0–Cu adsorbent. The elimination capability of the H3PO4

CNTFET-based ternary address decoder design
With the end of Moore's law, new paradigms are investigated for more scalable computing systems. One of the promising directions is to examine the data representation toward higher data density per hardware element. Multiple valued logic (MVL) emerged as a promising system due to its advantages over binary data representation. MVL offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared with binary systems. Accessing memory is considered one of the most power- and time-consuming instructions within a microprocessor. In the quest for building an entire ternary
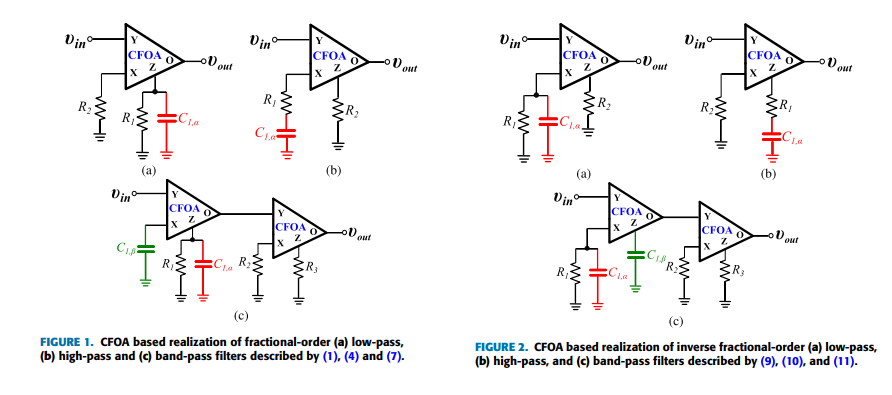
Non-Integer Order Generalized Filters Designs
Non-integer order filters can be derived from a generalized structure presented in this work. More specifically, fractional-order and power-law filters of single- or double-order are special cases of non-integer order filters with three degrees of freedom and can be implemented using a Current Feedback Operational Amplifier as the active element. The transfer function is formed as a ratio of two impedances which can be synthesized using Foster or Cauer RC networks. A curve-fitting based technique is employed for approximating the magnitude and phase of each impedance. The behavior of the
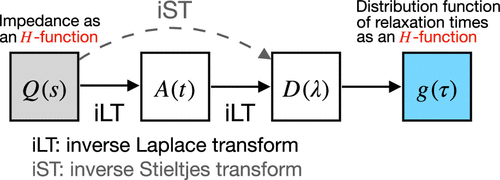
Procedure for Obtaining the Analytical Distribution Function of Relaxation Times for the Analysis of Impedance Spectra Using the Fox H-Function
The interpretation of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data by fitting them to equivalent circuit models has been a standard method of analysis in electrochemistry. However, the inversion of the data from the frequency domain to a distribution function of relaxation times (DFRT) has gained considerable attention for impedance data analysis as it can reveal more detailed information about the underlying electrochemical processes without requiring a priori knowledge. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide a general and practical procedure for obtaining analytically the DFRT from
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
