Breadcrumb

Interdigitated C-Patch Metamaterial Antenna for Terahertz Sensing
This paper proposes a metamaterial Terahertz sensor with detected sensitivity for biomedical applications. The proposed sensor consists of two interdigitated golden C-shaped structures on top of Teflon substrate that is backed by a gold layer. The absorption spectrum contains a peak resonance corresponding to the maximum absorption of the sensor. The proposed sensor has a maximum narrow-band absorption at 3.35 THz, with an average sensitivity of 2.256 THz/RIU and a quality factor of 22.3. The developed model is checked for the range of refractive index range between n= 1.3 to n= 1.4 to check

A (k,n)-Secret Image Sharing With Steganography Using Generalized Tent Map
Secret Image Sharing (SIS) transfers an image to mutually suspicious receivers as n meaningless shares, where k or more shares must be present to recover the secret. This paper proposes a (k, n)-SIS system for any image type using polynomial interpolation based on Lagrange polynomials, where the generated shares are of size 1/k of the secret image size. A full encryption system, consisting of substitution and permutation stages, is employed by using the generalized Tent map as a source of randomness. In addition to using a long and sensitive system key, steganography using the Least
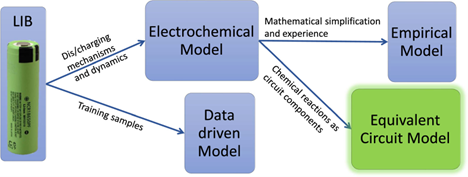
Fractional-Order Equivalent-Circuit Model Identification of Commercial Lithium-Ion Batteries
The precise identification of electrical model parameters of Li-Ion batteries is essential for efficient usage and better prediction of the battery performance. In this work, the model identification performance of two metaheuristic optimization algorithms is compared. The algorithms in comparison are the Marine Predator Algorithm (MPA) and the Partial Reinforcement Optimizer (PRO) to find the optimal model parameter values. Three fractional-order (FO) electrical equivalent circuit models (ECMs) of Li-Ion batteries with different levels of complexity are used to fit the electrochemical
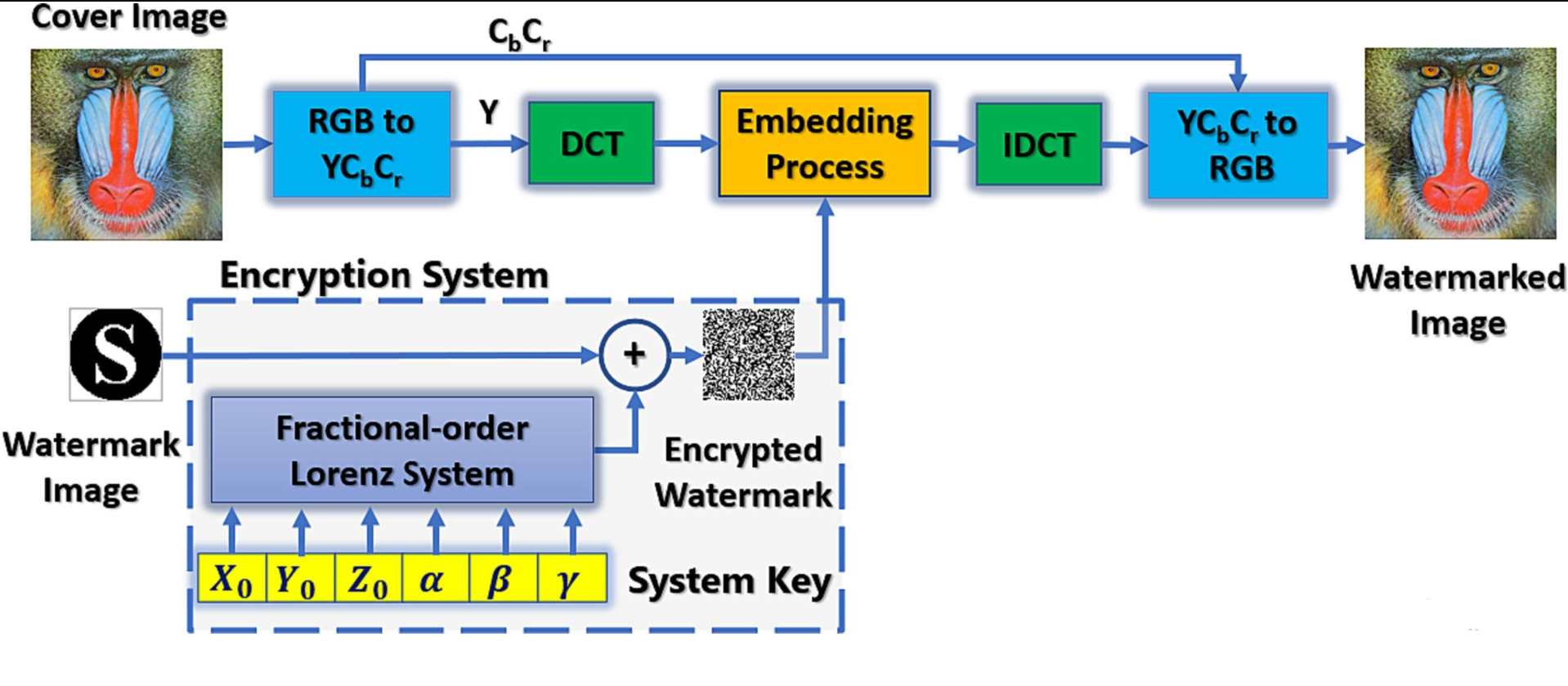
Secure blind watermarking using Fractional-Order Lorenz system in the frequency domain
This paper investigates two different blind watermarking systems in the frequency domain with the development of a Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG), based on a fractional-order chaotic system, for watermark encryption. The methodology is based on converting the cover image to the YCbCr color domain and applying two different techniques of frequency transforms, Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), to the Y channel. Then, the encrypted watermark is embedded in the middle-frequency band and HH band coefficients for the DCT and DWT, respectively. For more
Nonlinear fractional order boundary-value problems with multiple solutions
It is well-known that discovering and then calculating all branches of solutions of fractional order nonlinear differential equations with boundary conditions can be difficult even by numerical methods. To overcome this difficulty, in this chapter two semianalytic methods are presented to predict and obtain multiple solutions of nonlinear boundary value problems. These methods are based on the homotopy analysis method (HAM) and Picard method namely, predictor HAM and controlled Picard method. The used techniques are capable of predicting and calculating all branches of the solutions
Generalized synchronization of different dimensional integer-order and fractional order chaotic systems
In this work different control schemes are proposed to study the problem of generalized synchronization (GS) between integer-order and fractional order chaotic systems with different dimensions. Based on Lyapunov stability theory of integer-order differential systems, fractional Lyapunov-based approach and nonlinear controllers, different criterions are derived to achieve generalized synchronization. The effectiveness of the proposed control schemes are verified by numerical examples and computer simulations. © Springer International Publishing AG 2017.

Energy Harvesting Management Unit for Wearable Devices
Energy harvesting materials and systems have become a popular study topic that is rapidly expanding. The harvesters will be used for a variety of applications, including distributed wireless sensor nodes for structural health monitoring, embedded and implanted sensor nodes for medical applications, recharging large system batteries, monitoring pressure in automobiles, powering unmanned vehicles, and running security systems in domestic settings. Components and devices at micro-macro sizes, spanning materials, electronics, and integration, have recently been developed. Energy harvesting has

Wastewater Treatment: Recycling, Management, and Valorization of Industrial Solid Wastes
Wastewater Treatment: Recycling, Management, and Valorization of Industrial Solid Wastes bridges the gap between the theory and applications of wastewater treatments, principles of diffusion, and the mechanism of biological and industrial treatment processes. It presents the practical applications that illustrate the treatment of several types of data, providing an overview of the characterization and treatment of wastewaters, and then examining the different biomaterials and methods for the evaluation of the treatment of biological wastewaters. Further, it considers the various types of

Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Systems for Sustainable Medical Rooms and Enhanced Life Quality
Indoor air pollution poses a substantial risk to human health and well-being, underscoring the crucial requirement for efficient monitoring systems. This paper introduces an advanced Air Pollution Monitoring System (APMS) tailored explicitly for indoor settings. The APMS integrates sensors and a user interface, ensuring the delivery of real-time and precise data concerning air quality parameters such as particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon dioxide (CO2), as well as temperature and humidity. The proposed APMS has several advantages, including low maintenance
Memristor-based balanced ternary adder
This paper introduces a memristor based ternary adder, which is an essential building block for any arithmetic ternary operations. The proposed ternary adder circuit tries to achieve the theoretical advantages of the ternary system, increase the density and decrease the processing time by using the memristor properties such as its hysteresis and nanotechnology. The general block diagram of the proposed circuit is illustrated based on memristors and its operation has been validated via different examples using PSPICE where simulation results show a great match. © 2013 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
