Breadcrumb
Di- and tri- cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal using different prepared materials based Sargassum dentifolium algae, and iron oxide
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are highly toxic and carcinogenic compounds as they are low water solubility, hardly degradable and may persist in the environment for many years. Therefore, this study was directed to PAHs ‘anthracene and naphthalene’ removal using a combination method between adsorption and degradation using sunlight. Three adsorbent materials, iron oxide (Fe) alone, Sargassum dentifolium (S) alone, and mixture of Iron oxide and Sargassum dentifolium (FeS) were prepared. Afterwards, optimisation process was performed for the three adsorbent forms through some
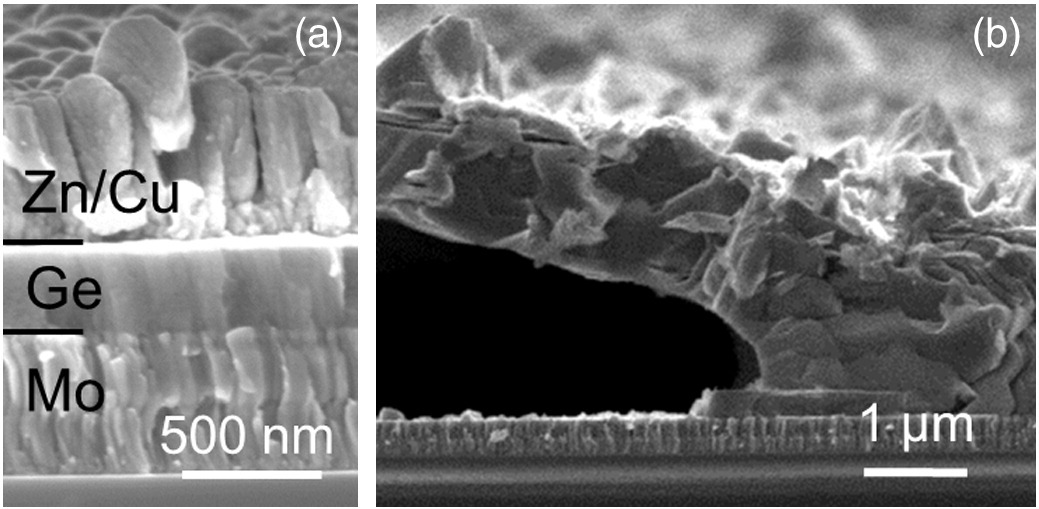
Physical characterization of Cu2ZnGeSe4thin films from annealing of Cu-Zn-Ge precursor layers
Cu2ZnGeSe4(CZGeSe) can be considered as a potential alternative for wide band gap thin film devices. In this work, CZGeSe thin films were deposited on Mo-coated soda lime glass substrates by sequential deposition of sputtered Cu, Zn and e-beam evaporated Ge layers from elemental targets followed by annealing at high temperature using H2Se gas. We report on the effect of the precursor stack order and composition and the impact of the annealing temperature on the physical properties of CZGeSe thin films. The optimal layer morphology was obtained when using a Mo/Cu/Zn/Ge precursor stack annealed
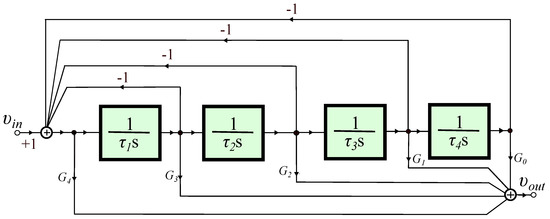
A 1 + α Order Generalized Butterworth Filter Structure and Its Field Programmable Analog Array Implementation
Fractional-order Butterworth filters of order 1 + (Formula presented.) (0
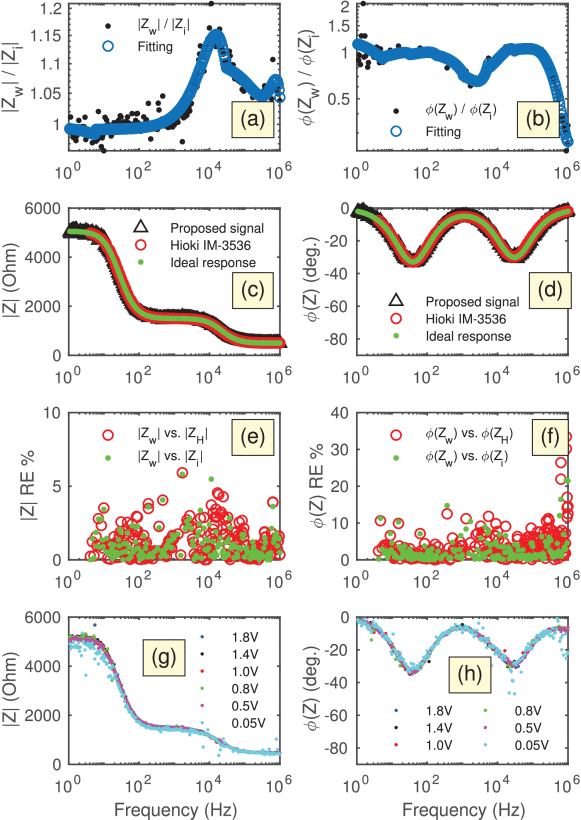
Time-Frequency Design of a Multi-Sine Excitation with Random Phase and Controllable Amplitude for (Bio) Impedance Measurements
Impedance spectroscopy has become a standard electroanalytical technique to study (bio)electrochemical and physiological systems. From an instrumentation point of view, the measurement of impedance can be carried out either in the frequency domain using the classical frequency sweep method or in the time domain using a variety of broadband signals. While time-domain techniques can be implemented with relatively simple hardware and can achieve faster acquisition time, they are still not that popular because of their lower accuracy and modularity. In this work we present a method and an

A collection of interdisciplinary applications of fractional-order circuits
An attractive feature of fractional calculus is its application in various interdisciplinary fields, extending from biomedical and biological notions to mechanical properties. For their description, fractional-order models have outperformed the corresponding integer-order models, resulting in a more realistic behavior, due to the additional degrees of freedom offered and the long-term memory effect that reflects the fractional order. These improved features are processed by appropriate circuit implementations, derived through several approximation methods, whose primary objective is to provide
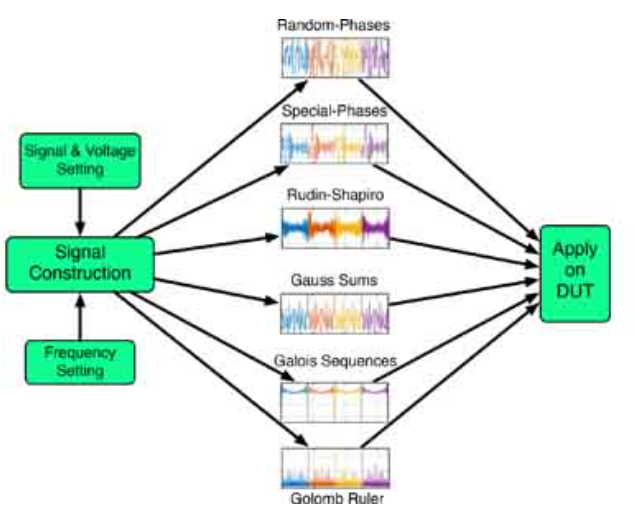
Wide Bandwidth Signals for Joint Time-Frequency Characterization of Nonlinear and Time-Varying Circuits
In this work, we generate and use a total of six different wideband signals for joint time-frequency characterization of nonlinear time-invariant [N-shaped differential resistor (NDR)] and linear time-varying (thermistor) circuits. A data acquisition board is used for applying the signals in the form of a voltage excitation and reading the induced current. The input signals have flat power spectra, thus avoiding the need for iterative calibration loops required to obtain signals with low crest factor. Such iterative loops are unavoidable when using random, pseudorandom, or chaotic signals all
MOS realizations of fractional-order elements
The exploitation of fractional calculus in engineering applications requires the utilization of fractional-order elements. As there is no immediate access to such type of elements, emulators that proportionally imitate their behavior are developed. The realization of emulators of fractional-order elements is based on the approximation of their impedance function. Subsequently, an advantageous option for the circuit implementation of the obtained, approximated impedance function is MOS transistor-based configurations, as they provide a dynamic system with electronically adjustable parameters

Reduce Computing Complexity of Deep Neural Networks Through Weight Scaling
Large deep neural network (DNN) models are computation and memory intensive, which limits their deployment especially on edge devices. Therefore, pruning, quantization, data sparsity and data reuse have been applied to DNNs to reduce memory and computation complexity at the expense of some accuracy loss. The reduction in the bit-precision results in loss of information, and the aggressive bit-width reduction could result in noticeable accuracy loss. This paper introduces Scaling-Weight-based Convolution (SWC) technique to reduce the DNN model size and the complexity and number of arithmetic
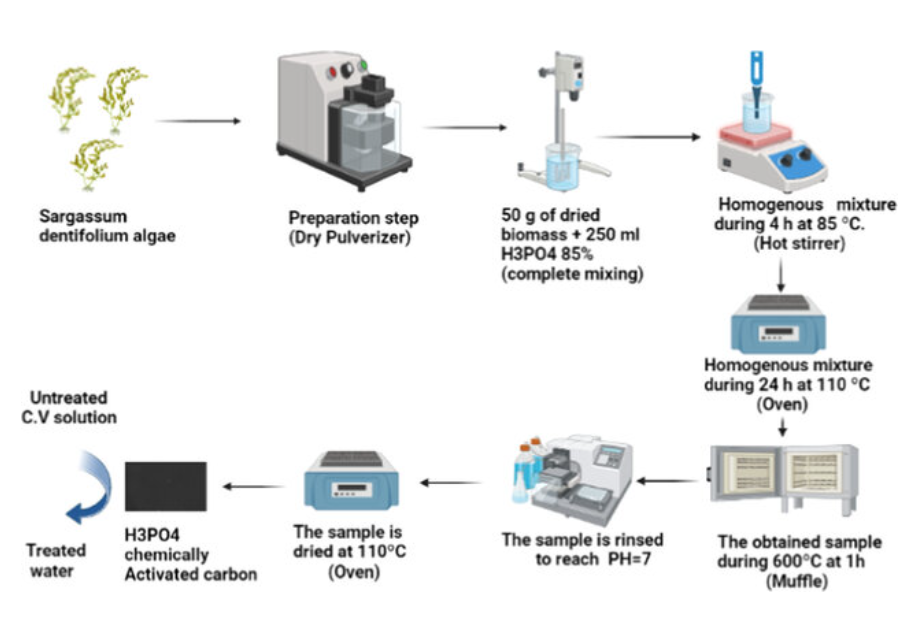
Crystal violet removal using algae-based activated carbon and its composites with bimetallic Fe0-Cu
The textile industry is considered a source of pollution because of the discharge of dye wastewater. The dye wastewater effluent has a significant impact on the aquatic environment. According to the World Bank, textile dyeing, and treatment contribute 17 to 20% of the pollution of water. This paper aims to prepare the bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0-Cu), algae-activated carbon, and their composites (AC-Fe0-Cu), which are employed as adsorbents. In this paper, Synthetic adsorbents are prepared and examined for the adsorption and removal of soluble cationic crystal violet (CV) dye
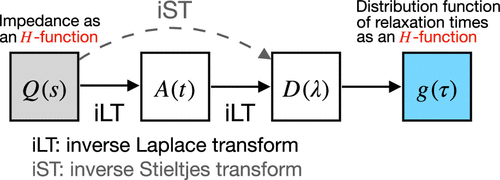
Procedure for Obtaining the Analytical Distribution Function of Relaxation Times for the Analysis of Impedance Spectra Using the Fox H-Function
The interpretation of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data by fitting them to equivalent circuit models has been a standard method of analysis in electrochemistry. However, the inversion of the data from the frequency domain to a distribution function of relaxation times (DFRT) has gained considerable attention for impedance data analysis as it can reveal more detailed information about the underlying electrochemical processes without requiring a priori knowledge. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide a general and practical procedure for obtaining analytically the DFRT from
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
