Breadcrumb
Modified kinetic-hydraulic UASB reactor model for treatment of wastewater containing biodegradable organic substrates
This paper addresses a modified kinetic-hydraulic model for up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor aimed to treat wastewater of biodegradable organic substrates as acetic acid based on Van der Meer model incorporated with biological granules inclusion. This dynamic model illustrates the biomass kinetic reaction rate for both direct and indirect growth of microorganisms coupled with the amount of biogas produced by methanogenic bacteria in bed and blanket zones of reactor. Moreover, the pH value required for substrate degradation at the peak specific growth rate of bacteria is
Fractional-Order Model (FOM) for high-strength substrate biodegradation in conventional UASB reactor
This paper introduces a Fractional-Order Model (FOM) of Up-flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor for wastewater treatment regarding high-strength substrate biodegradation. The model can investigate the biogas production rate as well as the specific growth rate of bacteria with extra degree of freedom. Also, the hereditary effect of resident biomass on substrate degradation is studied on periodically long terms. Moreover, biomass concentration is examined in reactor under the influence of various fractional orders. Several numerical simulation results are introduced based on Grünwald
Analytical solution for fractional derivative gas-flow equation in porous media
In this paper, we introduce an analytical solution of the fractional derivative gas transport equation using the power-series technique. We present a new universal transform, namely, generalized Boltzmann change of variable which depends on the fractional order, time and space. This universal transform is employed to transfer the partial differential equation into an ordinary differential equation. Moreover, the convergence of the solution has been investigated and found that solutions are unconditionally converged. Results are introduced and discussed for the universal variable and other
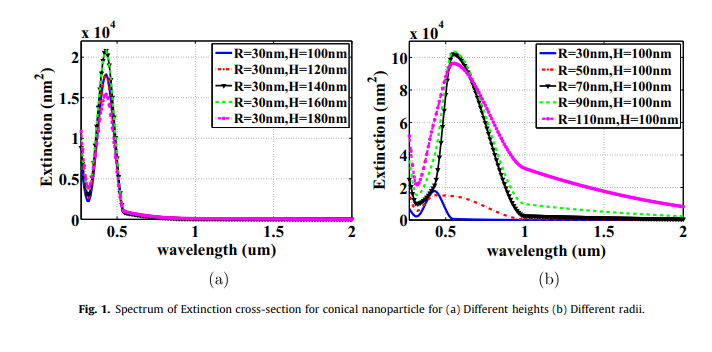
J-V characteristics of plasmonic photovoltaics with embedded conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics (PVs) are promising structures that improve thin-film photovoltaics performance, where optical absorption is improved via embedding metallic nanoparticles in the PV's active layer to trap the incident optical wave into the photovoltaic cell. The presented work investigates the design of PV with both structures of conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles through studying their extinction cross-sections and electric field distributions. Also, the impact of these nanoparticles in silicon PVs on the optical absorption enhancement is investigated. The figure of merit
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
