Breadcrumb
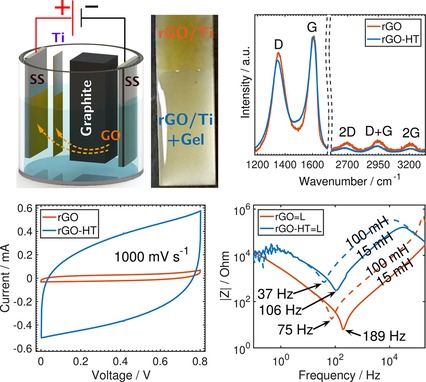
All-Solid-State Double-Layer Capacitors Using Binderless Reduced Graphene Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Bipolar Electrochemistry
Bipolar electrochemistry is used as an economical, single-step, and scalable process for the oxidation of a wireless graphite substrate, and the subsequent electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide thin film on a second wireless substrate. An all-solid-state symmetric double-layer capacitor (EDLC) using binderless reduced graphene oxide electrodes exhibited outstanding reversibility and capacitance retention over 18000 cycles, as well as superior capacitive behavior at far-from-dc frequencies (for example 45 and 47 µ F cm-2), effective capacitances at 75 and 189 Hz, respectively (computed
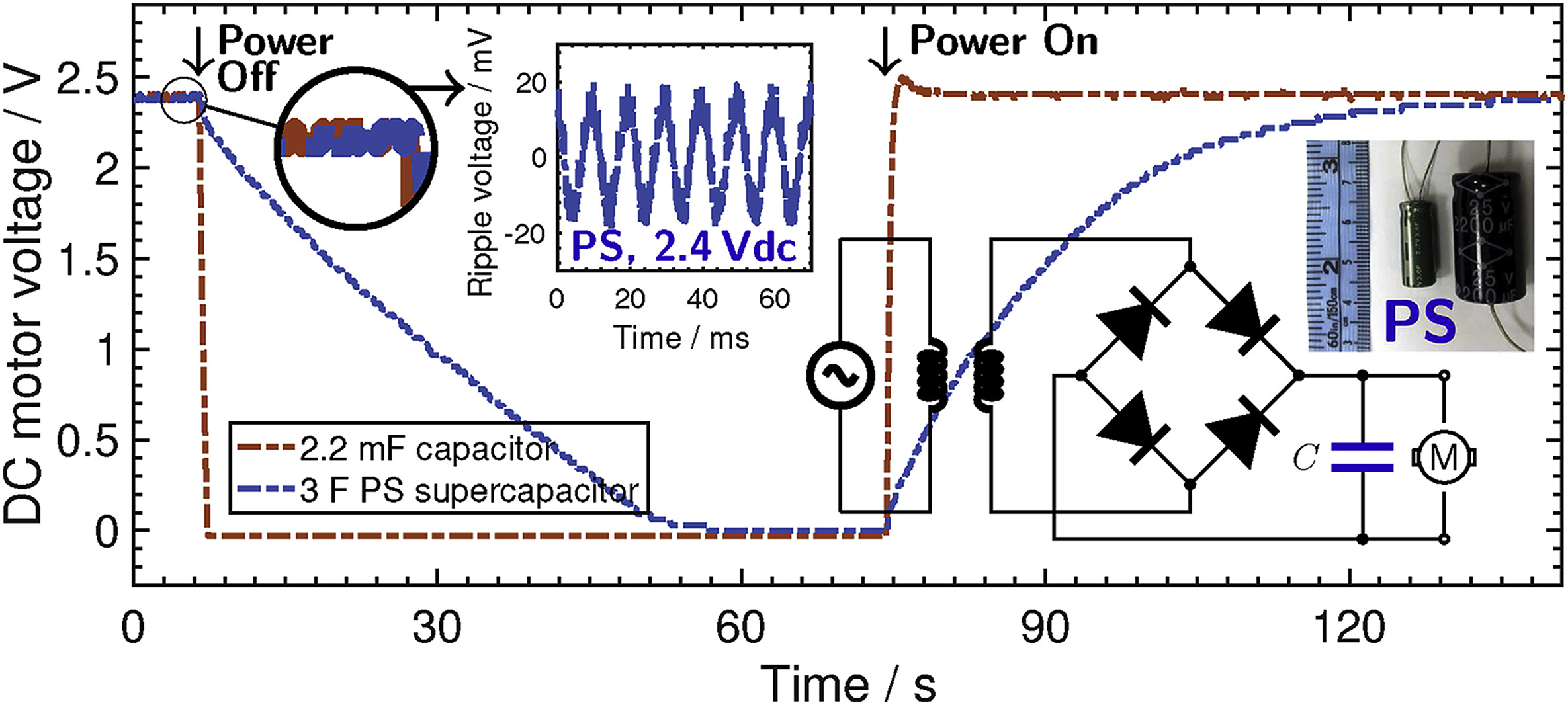
Capacitive behavior and stored energy in supercapacitors at power line frequencies
Supercapacitors are commonly viewed and mainly employed as dc electrical energy storage devices. Their behavior at far-from-dc is usually overlooked and not well explored for potential applications. In this work, we investigate analytically and experimentally the performance of supercapacitor at high frequencies, including the 50 Hz/60 Hz power line frequencies. The variation of effective capacitance, power and energy with frequency are analyzed using a fractional-order model consisting of a series resistance and a constant phase element for both pure sinusoidal and full-wave rectified voltage
Frational Order Inverse Filters Based on CCII Family
This paper proposes two generalized topologies of fractional order inverse filters (FOIF). All possible realizations of each topology are investigated using the second generation current conveyor (CCII) family. Inverse fractional highpass (IFHPF), inverse fractional bandpass (IFBPF), and inverse fractional lowpass (IFLPF) filters are realized using the same topology based on the generalized admittances. Numerical and P-Spice simulation results are presented for selected cases to approve the theoretical findings. The fractional order parameters increase the design flexibility and
Commercial supercapacitor parameter estimation from step voltage excitation
Supercapacitors are crucial elements in advanced industrial electronic systems particularly when supplied from renewable energy sources. Here, we derive expressions for the current, power, and stored energy in a supercapacitor excited with a step voltage signal. Although, it is not common practice to charge supercapacitors using a step voltage, these devices are sometimes used in switching-type applications where they are subject to this type of signal. We validate the derived mathematical expression of the current via experiments on four different commercial devices. By fitting the measured
Temperature-aware adaptive task-mapping targeting uniform thermal distribution in MPSoC platforms
As on-chip integration increases, the thermal distribution becomes spatially non-uniform and varies based on the power dissipation. In this paper, we introduce a temperature-aware task-mapping algorithm to prevent hotspots and achieve a highly uniform thermal distribution using adaptive multi-threshold values. The algorithm monitors the temperature of the cores, swaps tasks when the temperature of the core is relatively higher than the average temperature of the chip. Cores are switched off if they exceed an absolute maximum temperature. Using this algorithm, reliability is enhanced by
Interfacial modification of perovskite solar cell using zno electron injection layer with pdms as antireflective coating
Recently, perovskite solar cells (PSCs) exhibits tremendous power conversion efficiency and has shown enhanced figures of merit being secured regarding cell stability. In this paper, perovskite solar cell with Zno electron injection layer is presented. The humidity degradation of the perovskite active layer and the efficiency of the cell is observed under several conditions. Using ZnO as a planner electron injection layer (EIL) instead of TiO2, the efficiency of the device significantly improved, showing low-resistance shunting pathways. Also, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) has been used as a
Two-dimensional front-tracking model for film evaporation
To understand the physical process involved in film evaporation, a new numerical model is created using coupled quadratic finite element formulation of the conservation equations. The heat transport equation is solved in the three different phases (solid, liquid and vapor) while the Navier-Stokes equation are solved in the two fluids. The gradient discontinuity at the liquid vapor interface provides local value of the evaporative flux density that is directly linked to the interface velocity jump through mass conservation principle and used as boundary condition for two fluid flow computations
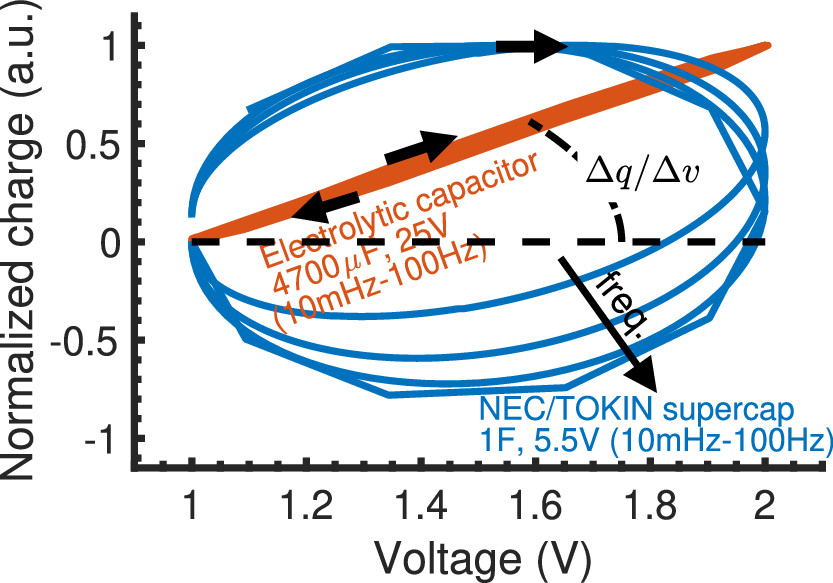
Highlighting a Common Confusion in the Computation of Capacitance of Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices
[No abstract available]
Frequency-dependent effective capacitance of supercapacitors using electrospun cobalt-carbon composite nanofibers
Mixing carbon-based materials with pseudocapacitive material is a widely used strategy to prepare high-energy, high-power supercapacitors. However, phase separation is inevitable after extended charging/discharging which leads to the degradation of performance metrics of the device. Here, we prepare in a single step cobalt-incorporated carbon nanofibers (CNF) by electrospinning homogeneous solutions of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) with cobalt acetate at different nominal proportions (1:0 to 1:1), and investigate their stability and capacitive behavior in symmetric supercapacitors. The
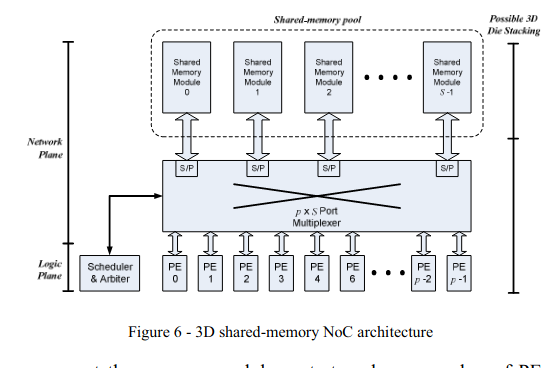
Novel 3D memory-centric NoC architecture for transaction-based SoC applications
Large and complex system-on-chip devices consisting of many processor cores, accelerators, DSP functions and many other processing and memory elements are becoming common in the semiconductor industry nowadays. To communicate, these processing and memory elements need to have a network-on-chip (NoC) that is scalable enough to support large number of elements and large bandwidth among other requirements. This paper evaluates the performance of the 2D memory-centric NoC architecture from throughput and latency perspective versus the Mesh topology. We also propose a memory-centric architecture
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
