Breadcrumb

Applied Techniques for Wastewater Treatment: Physicochemical and Biological Methods
Polluted water is one of the significant challenges facing the world nowadays, especially with the noticed water shortage recorded in the last period. Different treatment methods, physicochemical and biological, were presented for pollutant removal from polluted wastewater. This review discusses the treatment methods starting from the biological part to help reduction of organics, which are solids that appear in the wastewater. After that, the physicochemical techniques will be discussed as a second part of the treatment process to minimize the heavy metal, dyes, and other pollutants
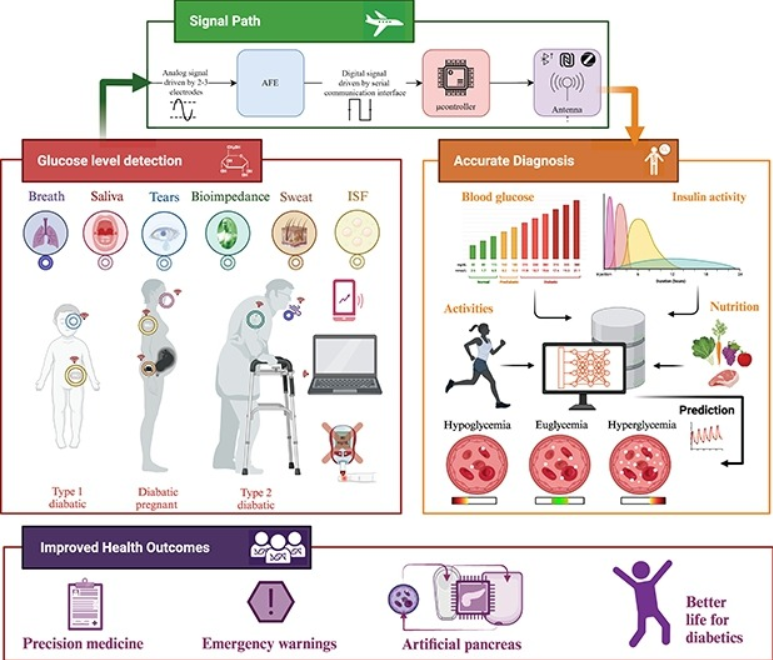
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive

Applied Techniques for Wastewater Treatment
Improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator
This paper presents an improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator which offers higher frequency and wider tunning range than the existing reactance-less oscillators. It also has the capability of operating on two positive supplies or alternatively a positive and negative supply. Furthermore, it has the advantage that it can be fully integrated on-chip providing an area-efficient solution. On the other hand, The oscillation concept is discussed then a complete mathematical analysis of the proposed oscillator is introduced. Furthermore, the power consumption of the new relaxation circuit is
Stochastic modeling of 2D photonic crystals
Due to the fabrication processes, inaccurate manufacturing of the photonic crystals (PCs) might occur which affect their performance. In this paper, we examine the effects of tolerance variations of the radii of the rods and the permittivity of the material of the two-dimensional PCs on their performance. The presented stochastic analysis relies on plane wave expansion method and Mote Carlo simulations. We focus on two structures, namely Si-Rods PCs and Air-Holes PCs. Numerical results show—for both structures—that uncertainties in the dimensions of the PCs have higher impact on its photonic
Communication-The Ragone Plot of Supercapacitors under Different Loading Conditions
The power-energy performance of supercapacitors is usually visualized by the Ragone plot of (gravimetric or volumetric) energy density vs power density. The energy is commonly computed from E = CV2/2, and the power from P = E/Δt, which assume RCbased models. In this study, we investigate the energy-power profiles of two commercial supercapacitors discharged with three different types of loads: (i) constant current, (ii) constant power, and (iii) constant resistive load. The energy is computed as per the definition from the time-integral of its instantaneous power, i.e. E(t) = ò p(t)dt with p(t
Communication—convolution-based estimation of supercapacitor parameters under periodic voltage excitations
Supercapacitors are typically used in applications requiring frequent and continuous charging/discharging cycles, but most of the models available in the literature are designed to predict their behavior for a single sequence. In this letter, we show first that the electrical response and metrics of supercapacitors under periodic voltage excitations can generally be obtained using Fourier series analysis and convolution operations of functions derived based on any suitable impedance model. We verified our analysis procedure with simulations using particle swarm optimization, and experiments
Resonant square-wave clock generator for low power applications
Power reduction is the main challenge facing circuit designers in their quest to utilize the full performance of new process technologies. A major portion of the power consumed in today's systems is due to the clock generation and distribution. Resonant clocking has been a promising technique to reduce the clock power dramatically. In this paper, a novel resonant clock generator circuit is proposed to reduce the dynamic power used for clock generation by almost 75%. Two configurations of the circuit are presented. The merit of this generator is most obvious in the ease of its implementation
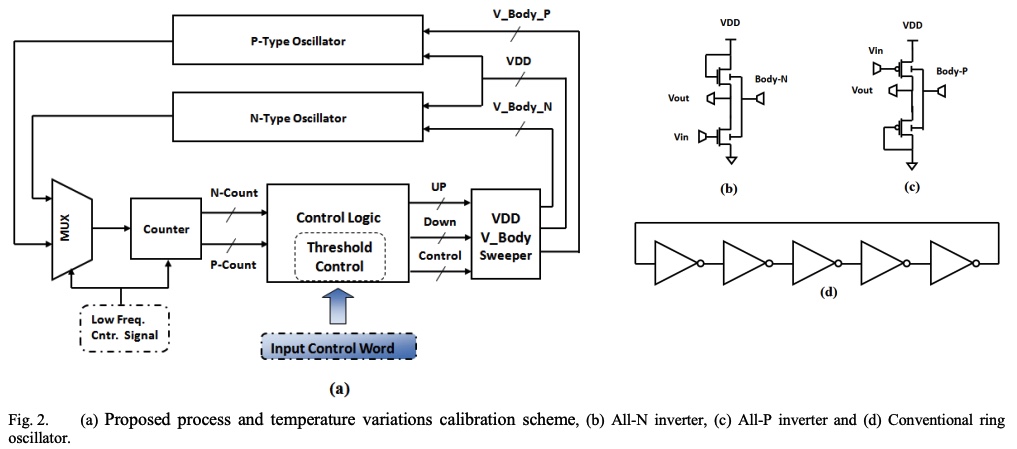
A dynamic calibration scheme for on-chip process and temperature variations
A process and temperature variation calibration scheme is proposed in this paper. The proposed system uses the supply voltage and body bias to calibrate the device parameters to match those of a certain process corner that is determined by the system designer. This scheme is characterized by its ability to dynamically change the desired mapping target according to the computational load. Moreover, the proposed system provides the ability to detect and control the n- and p-type variations independently through the use of an all-n and all-p ring oscillators. The calibration system has been
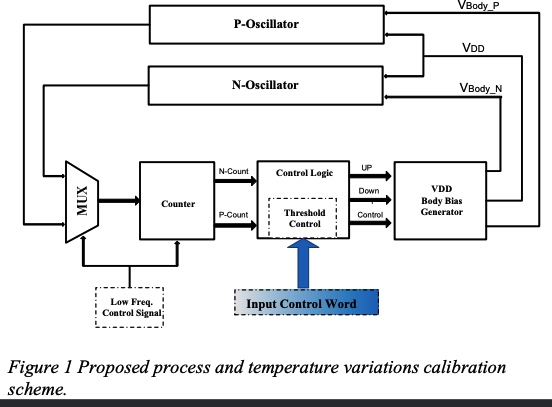
A dynamic power-aware process variation calibration scheme
In this paper, a power-aware process variation calibration scheme is proposed. The proposed calibration system provides the ability to detect and control the n- and p-type variations independently through the use of all-n and all-p ring oscillators. Calibration is then carried out through the use of the supply voltage and body bias to alter the device parameters to match those of a certain process corner that is determined by the system designer. This scheme is characterized by its ability to dynamically change the desired mapping target according to the computational load. The calibration
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››
