Breadcrumb
A power-aware task scheduler for energy harvesting-based wearable biomedical systems using snake optimizer
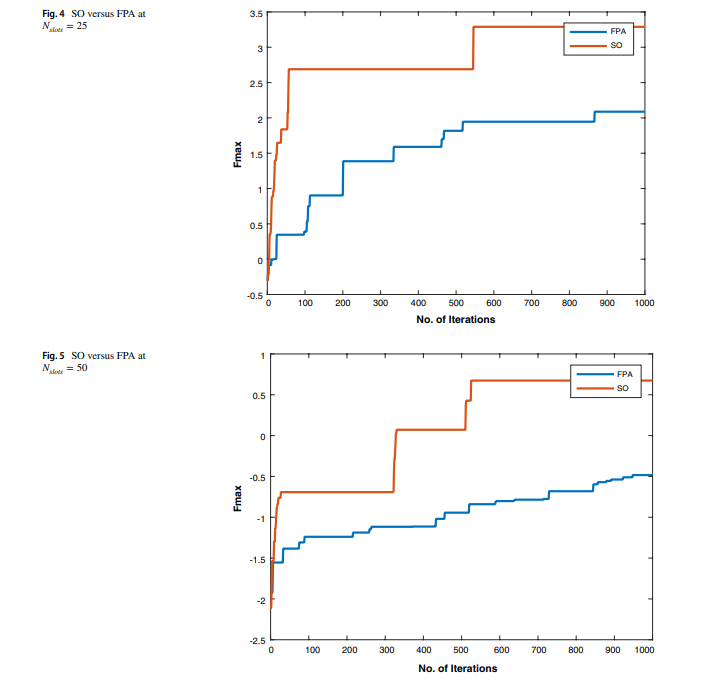
There is an increasing interest in energy harvesting for wearable biomedical devices. This requires power conservation and management to ensure long-term and steady operation. Hence, task scheduling algorithms will be used throughout this work to provide a reliable solution to minimize energy consumption while considering the system operation constraints. This study proposes a novel power-aware task scheduler to manage system operations. For example, we used the scheduler to handle system operations, including heart rate and temperature sensors. Two optimization techniques have been used to
An Efficient DMO Task Scheduling Technique for Wearable Biomedical Devices
The popularity of wearable devices has grown as they improve the quality of life in many applications. In particular, for medical devices, energy harvesters are the dominating source of energy for wearable devices. However, their power budget is limited. Thus, power-saving techniques are essential components in the whole technology stack of those devices. That is, choosing the optimal schedule for different tasks running on the wearable device can help to reduce energy consumption. This paper presents a sensor task scheduling technique for optimizing energy consumption for energy harvesting
Improvement of piezoresistive pressure sensor using zig-zag shaped and PVDF material
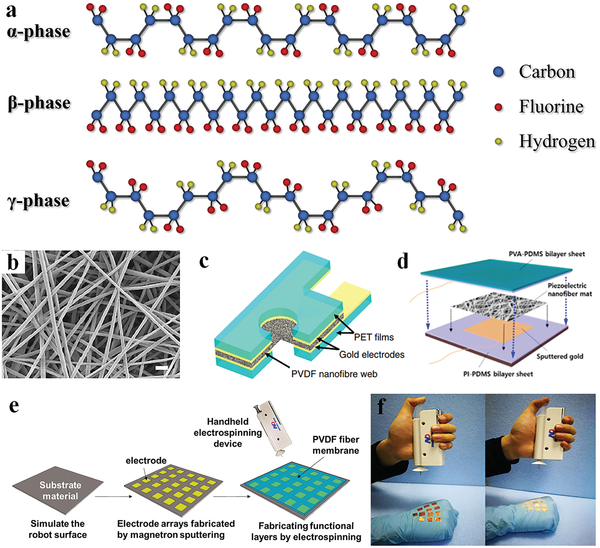
Due to a wide range of applications in the biomedical industry, the need for flexible and wearable sensors is growing every day. A pressure sensor generates a signal based on the applied pressure. Sensors have become an integral component of our daily lives, from personal gadgets to industrial machinery. The identification of the low signal from the body necessitates the use of particularly sensitive sensors. The development of a pressure sensor that can transform the maximum input signal into an electrical output is critical. In this paper, zig-zag piezoresistors on a square diaphragm were

Sustainable Energy-Aware Task Scheduling for Wearable Medical Device Using Flower Pollination Algorithm
Power management and energy conservation are crucial for medical wearable devices that rely on energy harvesting. These devices operate under strict power budgets and require prolonged and stable operation. To achieve this, Energy-aware task scheduling is proposed as a solution to minimize energy consumption while ensuring the continued operational capabilities of the device. our paper presents a task scheduling method using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). The proposed task scheduling focuses on managing the activity of key components such as the heart rate sensor, temperature sensor
SSHC with One Capacitor for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
Piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters have attracted a lot of attention as a way to power self-sustaining electronic systems. Furthermore, as part of the growing Internet of Things (loT) paradigm, the ongoing push for downsizing and higher degrees of integration continues to constitute major drivers for autonomous sensor systems. Two of the most effective interface circuits for piezoelectric energy harvesters are synchronised switch harvesting (SSH) on inductor and synchronous electrical charge extraction; nevertheless, inductors are essential components in both interfaces. This study
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
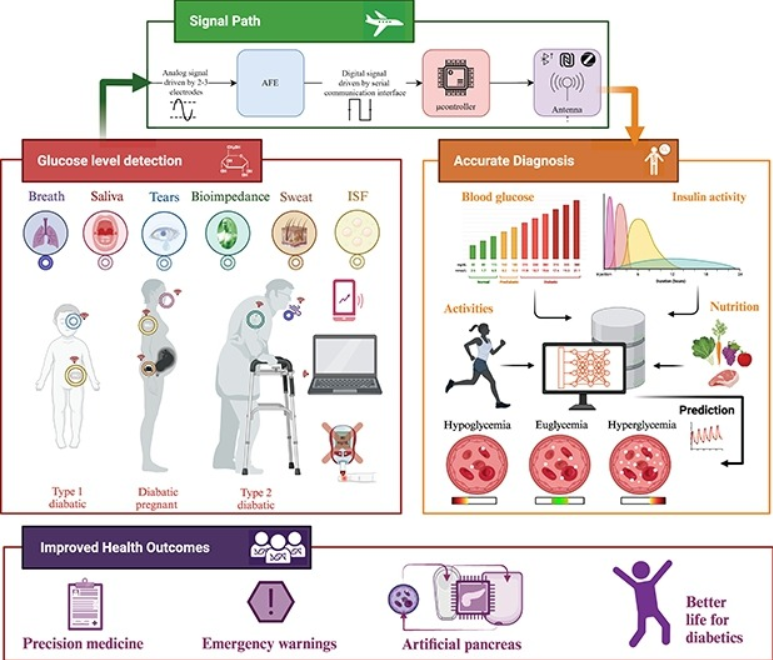
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive
A Comparative Analysis of Time Series Transformers and Alternative Deep Learning Models for SSVEP Classification
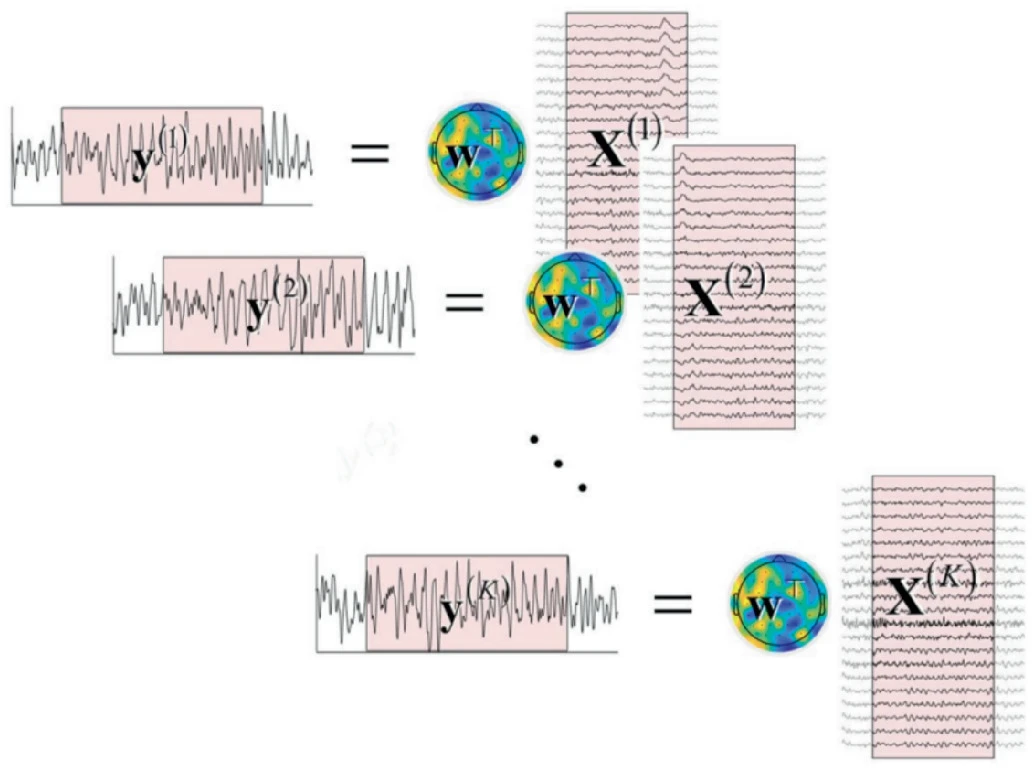
Steady State Visually Evoked Potentials (SSVEPs) are intrinsic responses to specific visual stimulus frequencies. When the retina is activated by a frequency ranging from 3.5 to 75 Hz, the brain produces electrical activity at the same frequency as the visual signal, or its multiples. Identifying the preferred frequencies of neurocortical dynamic processes is a benefit of SSVEPs. However, the time consumed during calibration sessions limits the number of training trials and gives rise to visual fatigue since there is significant human variation across and within individuals over time, which
Wireless Optogenetics Visual Cortical Prosthesis Control System
This research paper presents the wireless data and power transfer system for optogenetics visual cortical prosthesis. The system uses the inductive coupling power transfer and 2.4GHz Bluetooth 4.0 data transfer. This system contains two hardware parts: the external headset consists of power and data transmitters, image capture, and image processing units; the subcutaneous implant PCB consists of power and data receiver and the control unit. We also present the relative image processing method for this system. The whole system could power and control the optogenetic neural stimulus of the

Semi-Fragile Watermark for the Authentication and Recovery of Tampered Images
In order to strengthen the safety of corporate multimedia assets, a semi-fragile watermarking method is developed, which makes use of the integer wavelet transform (IWT) and the discrete cosine transform (DCT) for tamper detection and recovery. In this paper, we produce two distinct kinds of watermarks: an authentication watermark and a recovery watermark. A tamper detection methodology is utilized at the receiving end to check the watermarked image for validity and detect any assaults. If the changes are determined to be malicious, the suggested tamper recovery method is used to restore the
Realistic Wireless Smart-Meter Network Optimization Using Composite RPL Metric
In smart metering applications, transferring and collecting data within delay constraints is crucial. IoT devices are usually resource-constrained and need reliable and energy-efficient routing protocol. Furthermore, meters deployed in lossy networks often lead to packet loss and congestion. In smart grid communication, low latency and low energy consumption are usually the main system targets. Considering these constraints, we propose an enhancement in RPL to ensure link reliability as well as low latency. We refer to the proposed new additive composite metric as Delay-Aware RPL (DA-RPL)
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
