Breadcrumb
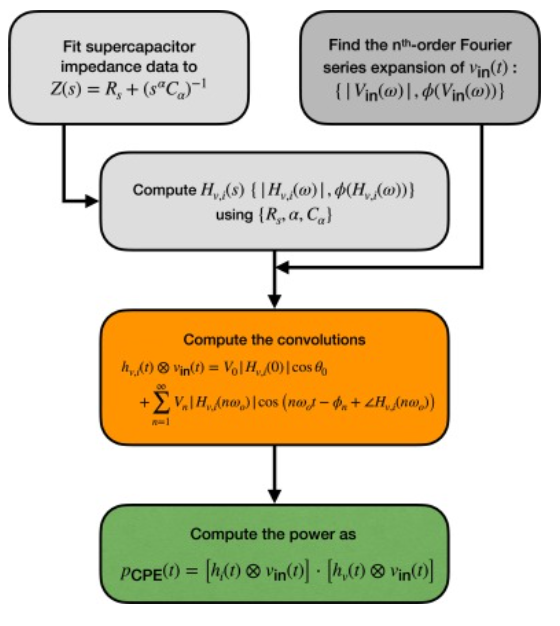
Time-domain response of supercapacitors using their impedance parameters and Fourier series decomposition of the excitation signal
Supercapacitors are mostly recognized for their high power density capabilities and fast response time when compared to secondary batteries. However, computing their power in response to a given excitation using the standard formulæof capacitors is misleading and erroneous because supercapacitors are actually non-ideal capacitive devices that cannot be characterized with a single constant capacitance. In this study we show how to estimate accurately the time-domain power and energy of supercapacitors in response to any excitation signal represented in terms of its Fourier series coefficients
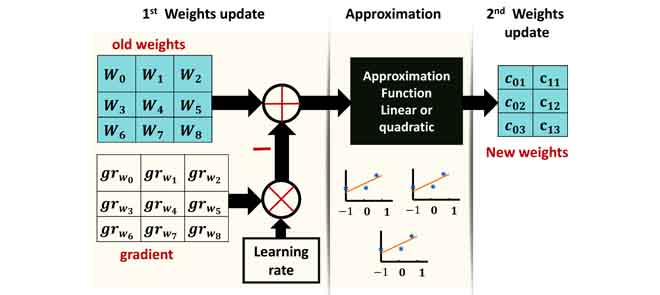
Deep Neural Networks-Based Weight Approximation and Computation Reuse for 2-D Image Classification
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are computationally and memory intensive, which present a big challenge for hardware, especially for resource-constrained devices such as Internet-of-Things (IoT) nodes. This paper introduces a new method to improve DNNs performance by fusing approximate computing with data reuse techniques for image recognition applications. First, starting from the pre-Trained network, then the DNNs weights are approximated based on the linear and quadratic approximation methods during the retraining phase to reduce the DNN model size and number of arithmetic operations. Then, the
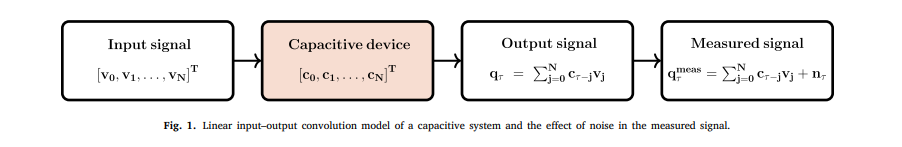
Tikhonov regularization for the deconvolution of capacitance from the voltage–charge response of electrochemical capacitors
The capacitance of capacitive energy storage devices cannot be directly measured, but can be estimated from the applied input and measured output signals expressed in the time or frequency domains. Here the time-domain voltage–charge relationship of non-ideal electrochemical capacitors is treated as an ill-conditioned convolution integral equation where the unknown capacitance kernel function is to be found. This comes from assuming a priori that in the frequency domain the charge is equal to the product of capacitance by voltage, which is in line with the definition of electrical impedance

Fractional-Order Modeling of Dynamic Systems with Applications in Optimization, Signal Processing and Control: Volume 2 in Emerging Methodologies and Applications in Modelling
Fractional-order Modelling of Dynamic Systems with Applications in Optimization, Signal Processing and Control introduces applications from a design perspective, helping readers plan and design their own applications. The book includes the different techniques employed to design fractional-order systems/devices comprehensively and straightforwardly. Furthermore, mathematics is available in the literature on how to solve fractional-order calculus for system applications. This book introduces the mathematics that has been employed explicitly for fractional-order systems. It will prove an
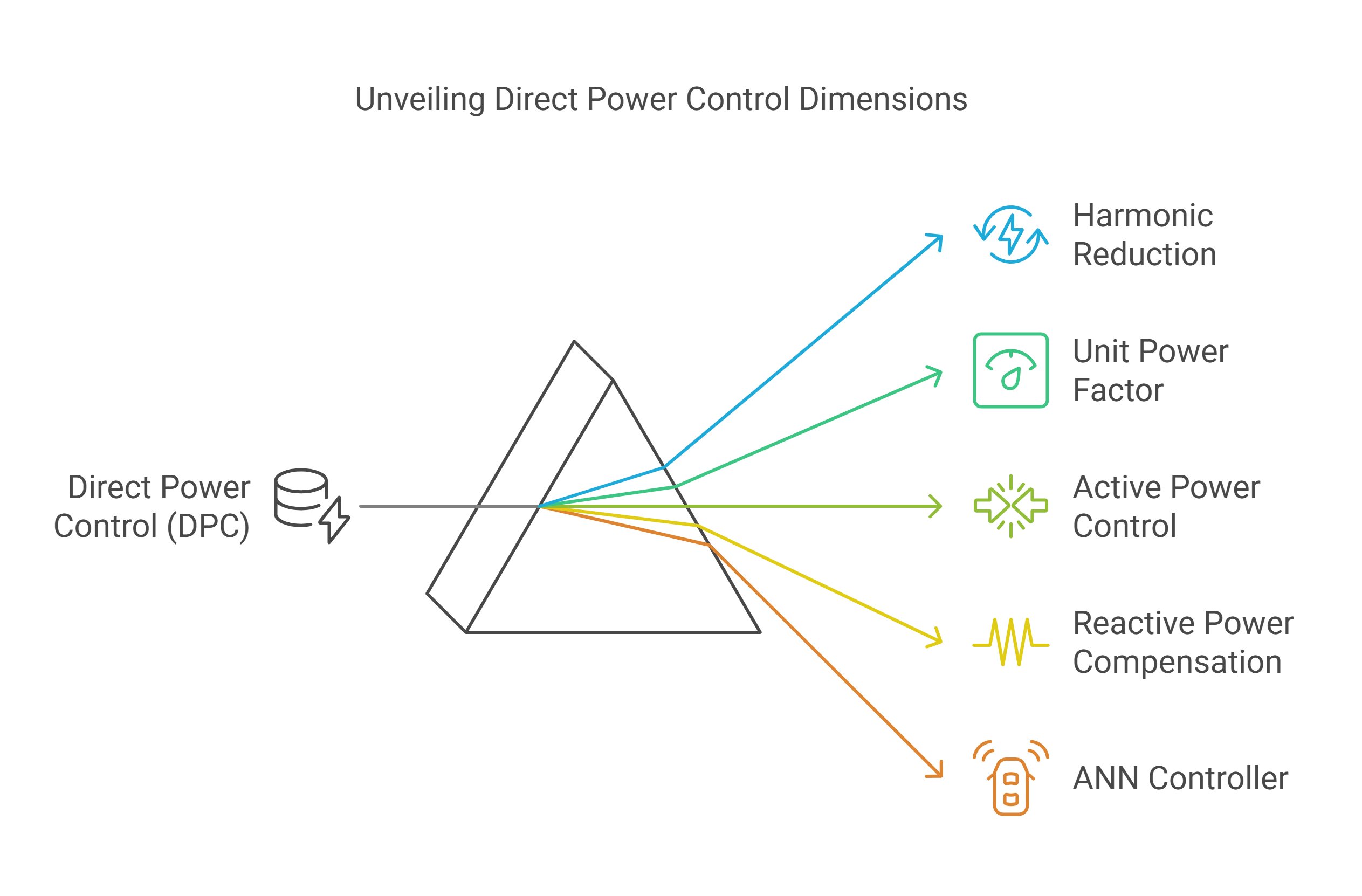
Artificial neural network for PWM rectifier direct power control and DC voltage control
In this chapter, a new technique has been proposed for reducing the harmonic content of a three-phase PWM rectifier connected to the networks with a unit power factor and also providing decoupled control of the active and reactive instantaneous power. This technique called direct power control (DPC) is based on artificial neural network (ANN) controller, without line voltage sensors. The control technique is based on well-known direct torque control (DTC) ideas for the induction motor, which is applied to eliminate the harmonic of the line current and compensate for the reactive power. The
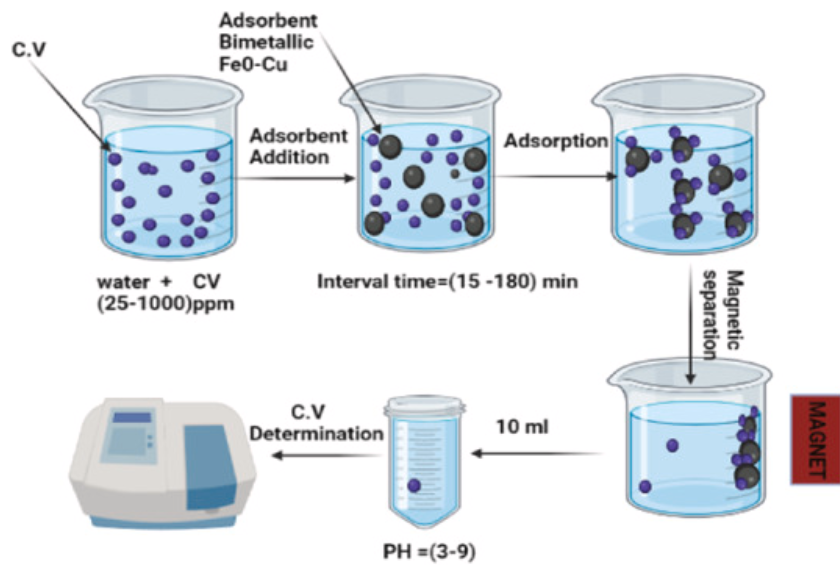
Crystal violet removal using bimetallic Fe0–Cu and its composites with fava bean activated carbon
Nano zero-valent iron (nZVI), bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0– Cu), and fava bean activated carbon-supported bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (AC-Fe0-Cu) are synthesized and characterized using DLS, zeta potential, FT-IR, XRD, and SEM. The maximum removal capacity is demonstrated by bimetallic Fe0–Cu, which is estimated at 413.98 mg/g capacity at pH 7, 180 min of contact duration, 120 rpm shaking speed, ambient temperature, 100 ppm of C.V. dye solution, and 1 g/l dosage. The elimination capability of the H2SO4 chemical AC-Fe0-Cu adsorbent is 415.32 mg/g under the same
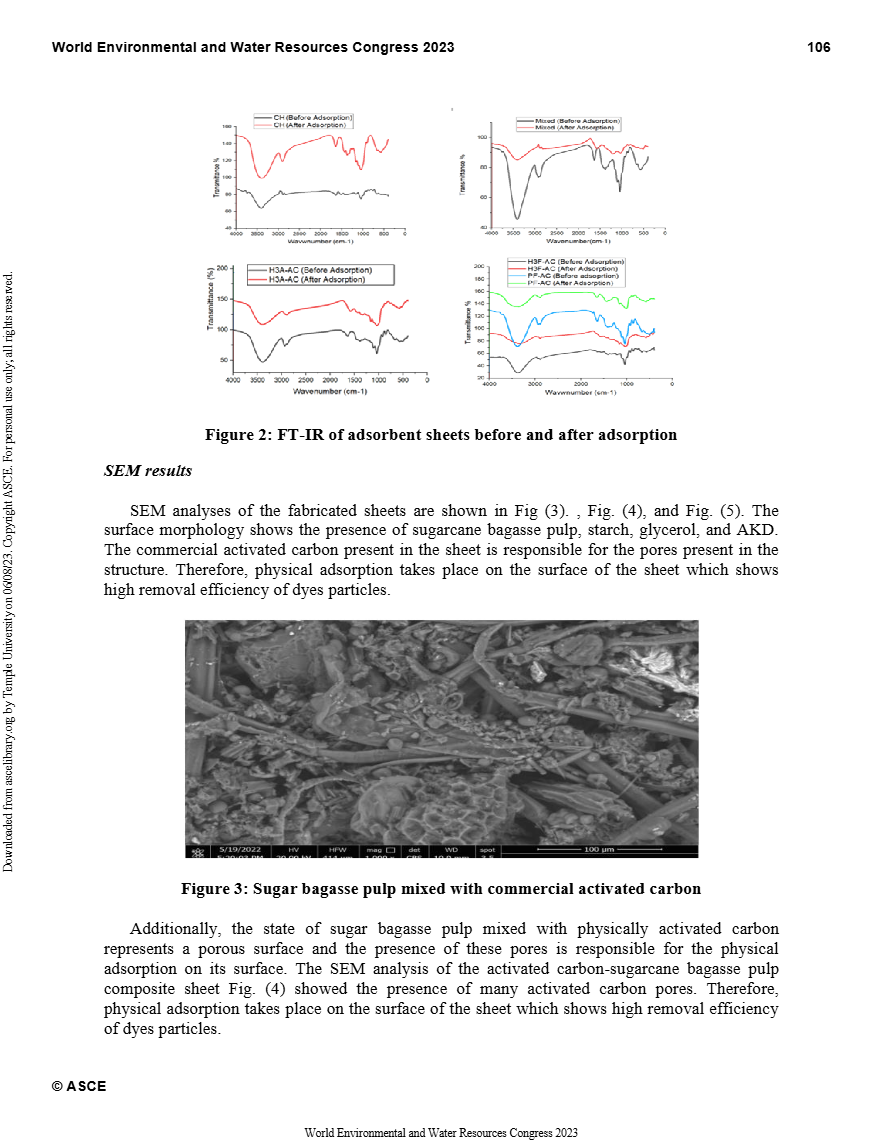
Valorization of Agricultural and Marine Waste for Fabrication of Bio-Adsorbent Sheets
Industrial wastewater often contains considerable amounts of toxic pollutants that would endanger public health and the environment. In developing countries, these toxins are often discharged into natural ecosystems without pretreatment as it requires costly treatment processes, which causes long-term harmful socioeconomic impacts. Employing wastewater treatment plants using physical, biological, and chemical methods to clean the wastewater is considered by many nations the answer to the environmental crises. The treated water could be used for targeting the irrigation systems in its majority
Robust adaptive supervisory fractional order controller for optimal energy management in wind turbine with battery storage
To address the challenges of poor grid stability, intermittency of wind speed, lack of decision-making, and low economic benefits, many countries have set strict grid codes that wind power generators must accomplish. One of the major factors that can increase the efficiency of wind turbines (WTs) is the simultaneous control of the different parts in several operating area. A high performance controller can significantly increase the amount and quality of energy that can be captured from wind. The main problem associated with control design in wind generator is the presence of asymmetric in the

In-Memory Associative Processors: Tutorial, Potential, and Challenges
In-memory computing is an emerging computing paradigm that overcomes the limitations of exiting Von-Neumann computing architectures such as the memory-wall bottleneck. In such paradigm, the computations are performed directly on the data stored in the memory, which highly reduces the memory-processor communications during computation. Hence, significant speedup and energy savings could be achieved especially with data-intensive applications. Associative processors (APs) were proposed in the seventies and recently were revived thanks to the high-density memories. In this tutorial brief, we
Deep Learning Based Kinematic Modeling of 3-RRR Parallel Manipulator
This paper presents a novel low cost design for a 3-RRR Planar Parallel Manipulator (PPM). These manipulators proved their superiority over serial manipulators due to their speed, precision and smaller work space where the work space area is accounted for in the design to ensure that the robot is performing its task in a smooth and simple way without getting into any singularity points. The challenge with PPM is to obtain the kinematic constraint equations of the manipulator due to their complex non-linear behavior. Screw theory is a new approach that is used to compute the direct and inverse
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
