Breadcrumb

Pixel-based Visual Secret Sharing Using Lorenz System
(n, n)-Visual Secret Sharing (VSS) allows a user to send an image in the form of shares to different participants. Every share can not reveal the secret alone, and only all shares together can reveal the secret with fast recovery. This paper proposes a pixel-based (n, n)-VSS system, where to share a pixel from the secret image, (n - 1) random pixels are generated from the Lorenz chaotic system for a varying set of (n - 1) shares. Then, the nth pixel is calculated for a random share using the secret pixel and the generated (n - 1) random pixels. The system is efficient, lossless, implemented
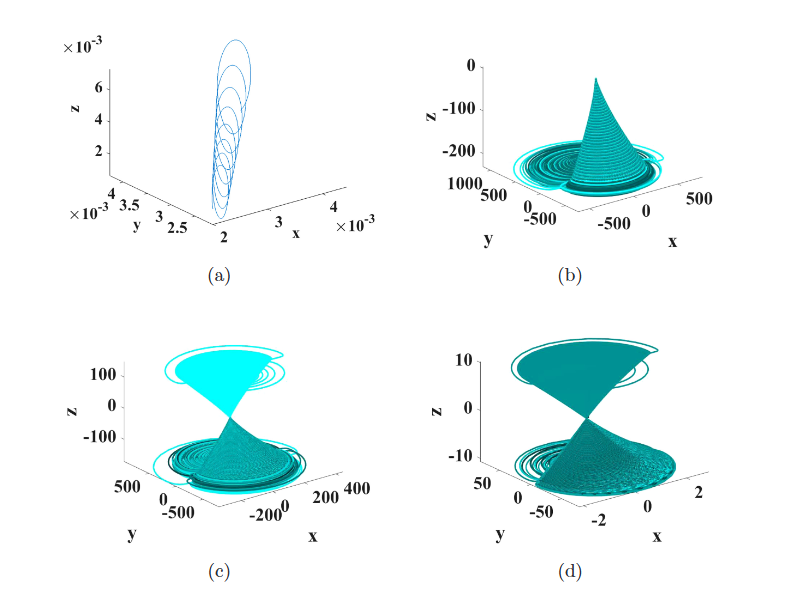
Numerical Sensitivity Analysis and Hardware Verification of a Transiently-Chaotic Attractor
We introduce a new chaotic system with nonhyperbolic equilibrium and study its sensitivity to different numerical integration techniques prior to implementing it on an FPGA. We show that the discretization method used in numerically integrating the set of differential equations in MATLAB and Mathematica does not yield chaotic behavior except when a low accuracy Euler method is used. More accurate higher-order numerical algorithms (such as midpoint and fourth-order Runge-Kutta) result in divergence in both MATLAB and Mathematica (but not Python), which agrees with the divergence observed in an

Fractional-Order Design: Devices, Circuits, and Systems: Volume 3 in Emerging Methodologies and Applications in Modelling
Fractional-Order Design: Devices, Circuits, and Systems introduces applications from the design perspective so that the reader can learn about, and get ready to, design these applications. The book also includes the different techniques employed to comprehensively and straightforwardly design fractional-order systems/devices. Furthermore, a lot of mathematics is available in the literature for solving the fractional-order calculus for system application. However, a small portion is employed in the design of fractional-order systems. This book introduces the mathematics that has been employed

Bowtie-Shaped Plasmonic Nanoparticles-Enhanced Photovoltaic Anti-Reflective Coating
Light trapping is a promising technique that enhances sunlight absorption by solar cells. This paper presents a study of bow-tie-shaped nanoparticles embedded in the antireflection coating of photovoltaic solar cells, which enhances the optical transmission of the photovoltaic surface. Therefore, the optical path length for light penetration is increased through the semiconductor active layer. First, the fundamental electric field modes of a single nanoscaled bow-tie are examined under excitation of plane waves with different polarizations. Second, an array of bow-tie-shaped nanoparticles is

Enhancing the Performance of Thin Film Photovoltaic Solar Cells using Truncated Conical Nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics are considered as promising photovoltaic candidate with enhanced optical absorption and quantum efficiency by embedding metallic nanoparticles in the photovoltaic active layer. In this paper, the efficiency enhancement of ultra-thin film solar cells with embedded truncated cone nanoparticles is studied. First, the natural electric field modes of the truncated cone in free-space are examined when excited by a plane wave. Parametric study is then performed to investigate the effects of the geometrical parameters of the structure on its resonant modes. Second, a uniform
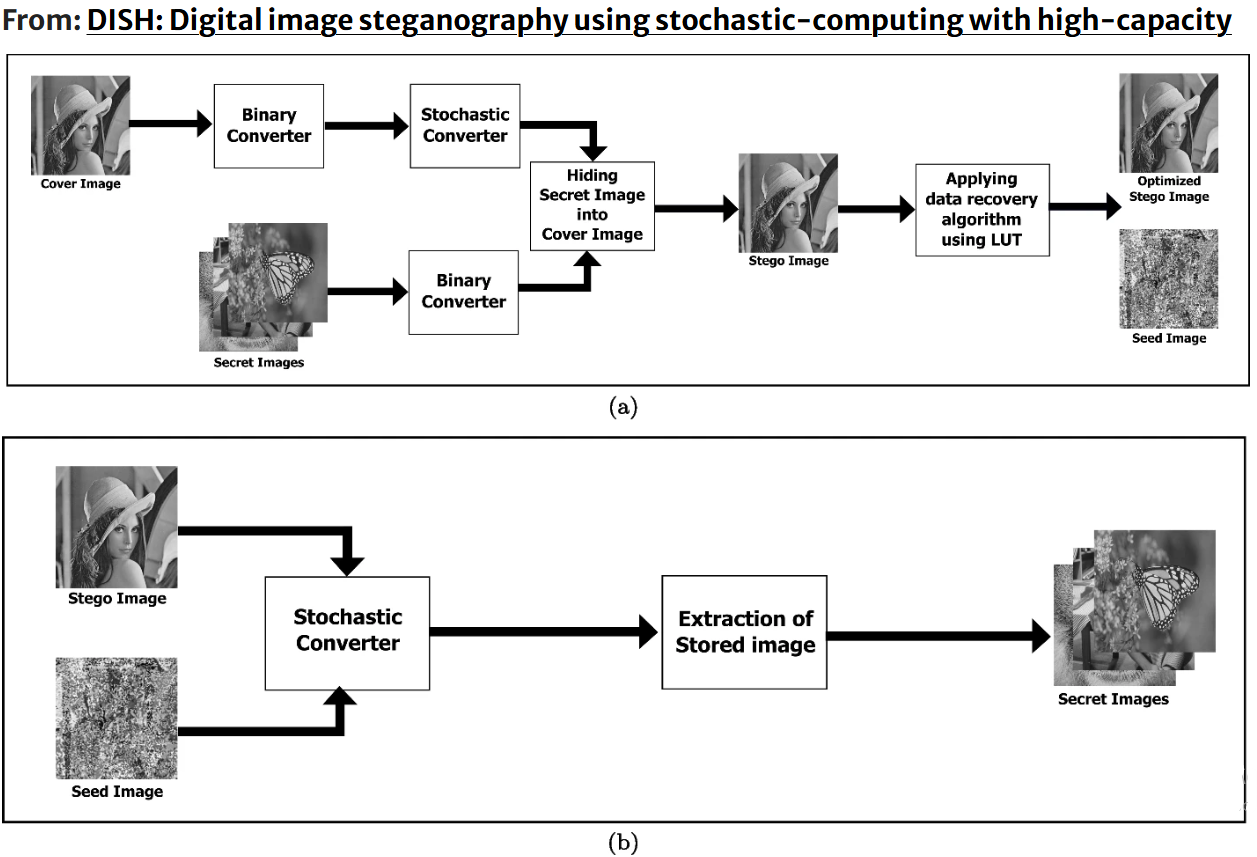
DISH: Digital image steganography using stochastic-computing with high-capacity
Stochastic computing is a relatively new approach to computing that has gained interest in recent years due to its potential for low-power and high-noise environments. It is a method of computing that uses probability to represent and manipulate data, therefore it has applications in areas such as signal processing, machine learning, and cryptography. Stochastic steganography involves hiding a message within a cover image using a statistical model. Unlike traditional steganography techniques that use deterministic algorithms to embed the message, stochastic steganography uses a probabilistic
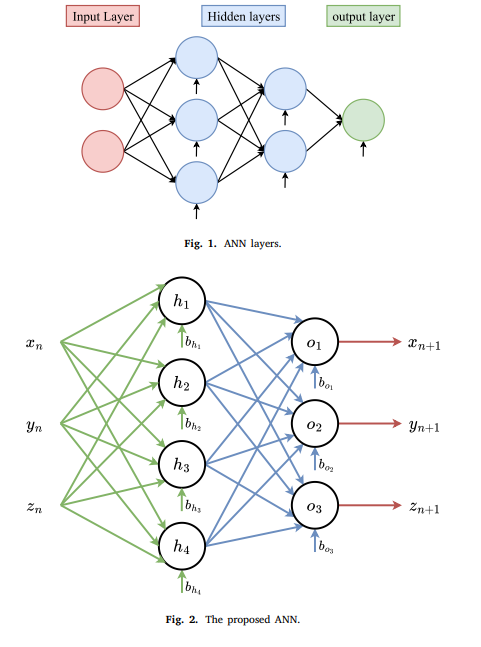
Artificial Neural Network Chaotic PRNG and simple encryption on FPGA
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are remarkably able to fit complex functions, making them useful in various applications and systems. This paper uses ANN to fit the Pehlivan–Uyaroglu Chaotic System (PUCS) to produce an Artificial Neural Network Chaotic Pseudo-Random Number Generator (ANNC-PRNG). The proposed PRNG imitates the PUCS chaotic system's properties and attractor shape. The proposed ANNC-PRNG is implemented in a simple image encryption system on the Xilinx Kintex-7 Genesys 2 Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) board. Hardware realization of an ANN trained on chaotic time series has
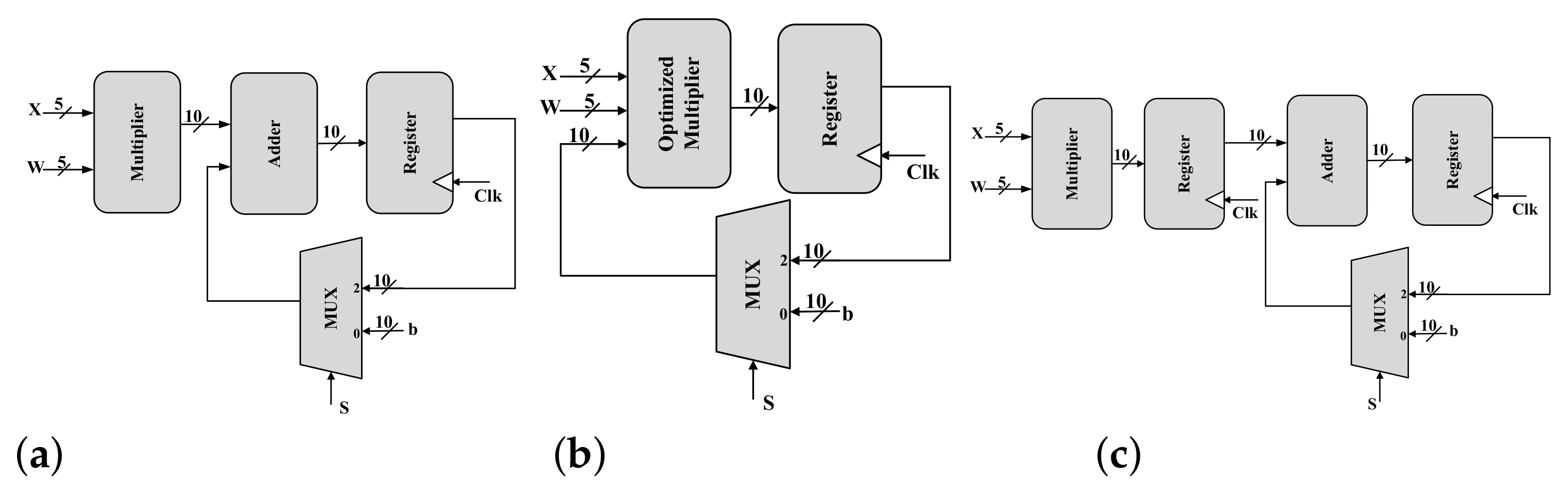
CNTFET-Based Ternary Multiply-and-Accumulate Unit
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) is one of the most commonly used operations in modern computing systems due to its use in matrix multiplication, signal processing, and in new applications such as machine learning and deep neural networks. Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. In this paper, a MAC is proposed using a CNTFET-based ternary logic number. Specifically, we build a 5-trit multiplier and 10-trit adder as building blocks of two ternary MAC unit designs. The first is a basic MAC which has two methods to

Different Approximation Techniques For A FOPID Feedback Control of a DC Motor
DC motors are commonly employed in many industrial applications due to their various advantages. This study aims to compare the response of the Oustaloup-Recursive-Approximation (ORA) and El-Khazali's approximation method in controlling a DC motor with a FOPID controller. The two employed methods are used to design the FOPID and approximate. For various fractional orders, many behaviours are presented. A simulation comparison between these methods is performed regarding overshoot, settling time and rise time. © 2022 IEEE.
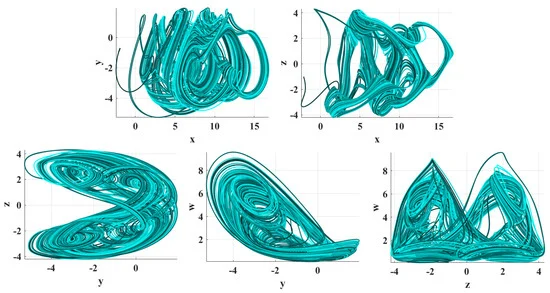
An Encryption Application and FPGA Realization of a Fractional Memristive Chaotic System
The work in this paper extends a memristive chaotic system with transcendental nonlinearities to the fractional-order domain. The extended system’s chaotic properties were validated through bifurcation analysis and spectral entropy. The presented system was employed in the substitution stage of an image encryption algorithm, including a generalized Arnold map for the permutation. The encryption scheme demonstrated its efficiency through statistical tests, key sensitivity analysis and resistance to brute force and differential attacks. The fractional-order memristive system includes a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
