Breadcrumb
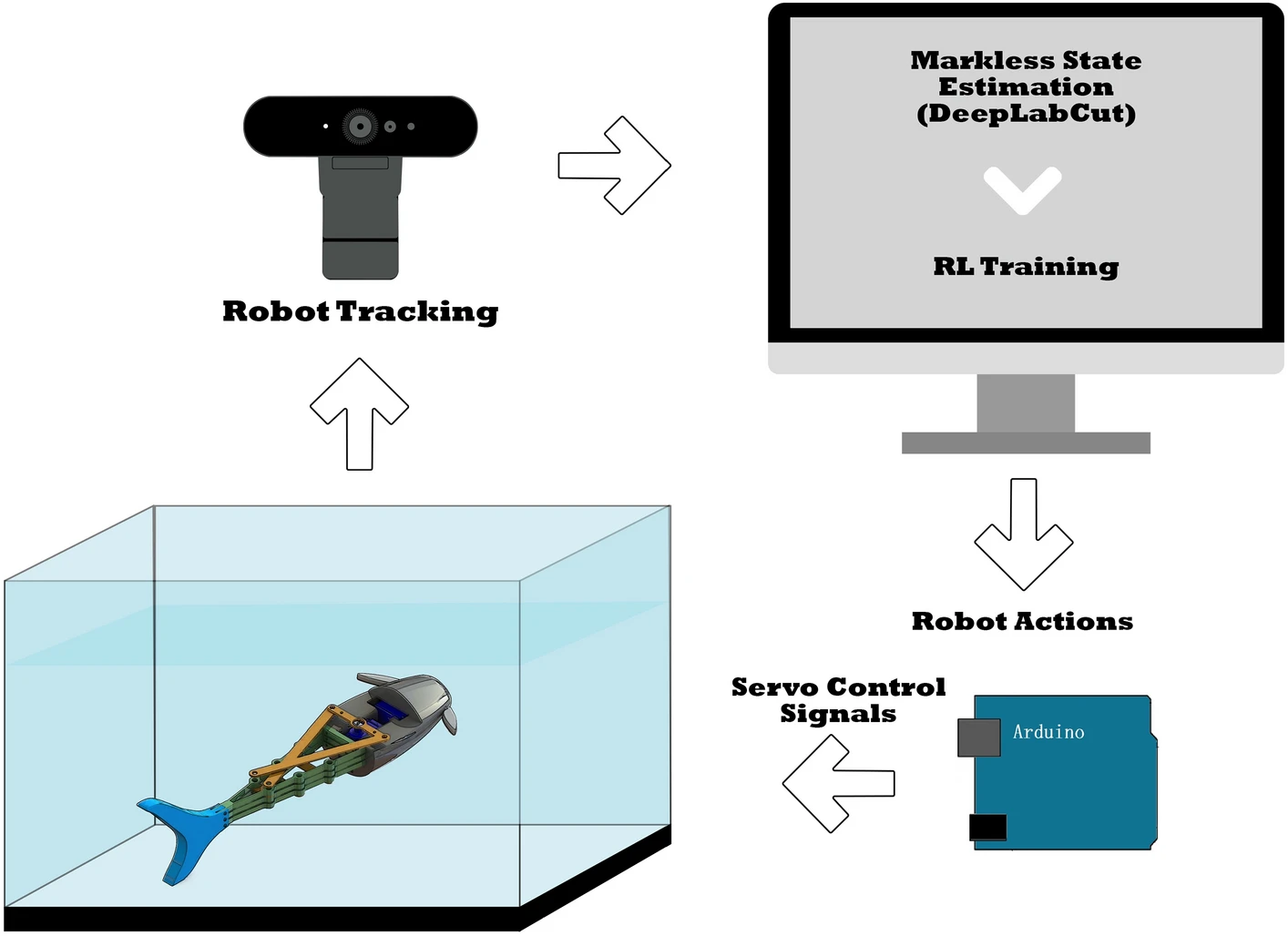
Design and control of soft biomimetic pangasius fish robot using fin ray effect and reinforcement learning
Soft robots provide a pathway to accurately mimic biological creatures and be integrated into their environment with minimal invasion or disruption to their ecosystem. These robots made from soft deforming materials possess structural properties and behaviors similar to the bodies and organs of living creatures. However, they are difficult to develop in terms of integrated actuation and sensing, accurate modeling, and precise control. This article presents a soft-rigid hybrid robotic fish inspired by the Pangasius fish. The robot employs a flexible fin ray tail structure driven by a servo

Battery Modeling with Mittag-Leffler Function
In various areas of life, rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are the technology of choice. Equivalent circuit models are utilized extensively in characterizing and modeling energy storage systems. In real-time applications, several generic-based battery models are created to simulate the battery's charging and discharging behavior more accurately. In this work, we present two generic battery models based on Mittag-Leffler function using a generic Standard battery model as a reference. These models are intended to fit the continuous discharging cycles of lithium-ion, Nickel-cadmium, and Nickel
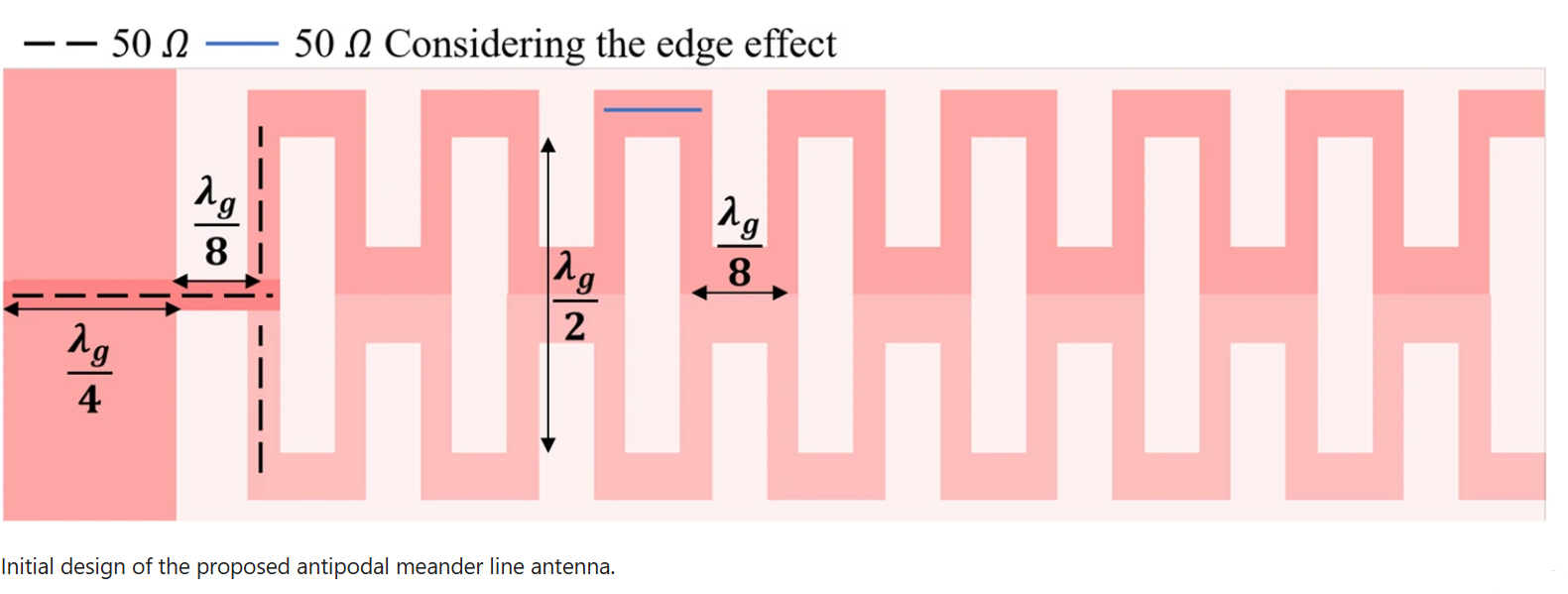
High gain antipodal meander line antenna for point-to-point WLAN/WiMAX applications
This paper introduces a planar antipodal meander line antenna fabricated using RO3003 substrate. The proposed antenna is designed to radiate in the end-fire direction, achieving a maximum measured gain of 10.43 dBi within its working bandwidth, which ranges from 2.24 GHz to 2.7 GHz, covering long-range WLAN/WiMAX applications. A systematic procedure is adopted in the design process to prove its tunability to cover other application requirements in terms of gain and bandwidth. The proposed design steps show that the bandwidth and the gain can independently be controlled by adjusting specific

High Gain Meander Line Antenna for 2.4 GHz Bluetooth Applications
In this paper, a highly directive meander line antenna is proposed to be utilized in the unlicensed Bluetooth band. The main goal of the proposed structure is to achieve low profile, and high gain in the Bluetooth band. Moreover, the antenna should be of low cost to be suitable for commercial use. The proposed structure is simulated using HFSS and CST to verify the obtained results. The maximum calculated gain of the antenna is 9.95 dBi (9.79 dBi) along the end-fire direction as simulated by HFSS (CST). The antenna demonstrated high radiation efficiency which is around 96% over its working
Fractional-order and memristive nonlinear systems: Advances and applications
[No abstract available]
On the generalization of fractional-order transmission lines
This paper demonstrates some fundamentals concerning the study of the Fractional order Transmission Line (FTL) operation. A numerical algorithm applied to study the transient analysis is shown describing the abnormal diffusion that appears in the operation of the TL. According to the steady state analysis of the FTL operation, the superior advantages over the conventional domain of imposing the fractional parameters are shown in this work. Moreover, all the conventional formulas are retrieved from the corresponding fractional ones by setting all fractional derivatives to unity. © 2014 IEEE.
A generalized framework for elliptic curves based PRNG and its utilization in image encryption
In the last decade, Elliptic Curves (ECs) have shown their efficacy as a safe fundamental component in encryption systems, mainly when used in Pseudorandom Number Generator (PRNG) design. This paper proposes a framework for designing EC-based PRNG and maps recent PRNG design techniques into the framework, classifying them as iterative and non-iterative. Furthermore, a PRNG is designed based on the framework and verified using the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) statistical test suite. The PRNG is then utilized in an image encryption system where statistical measures
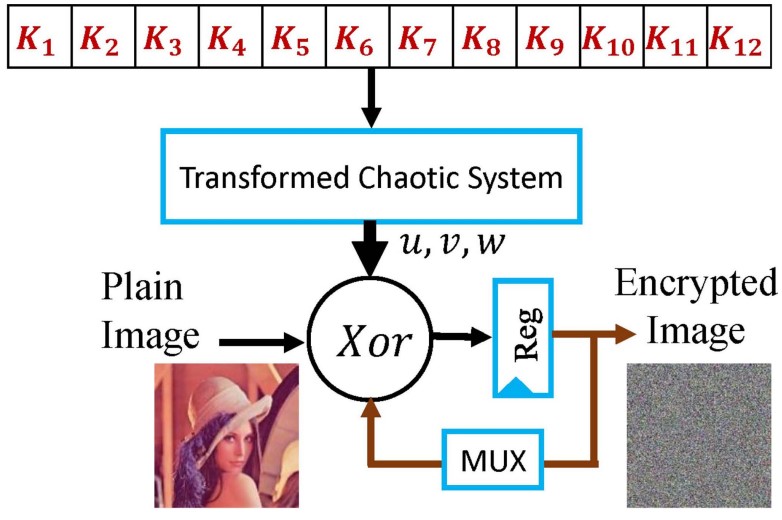
Self-Reproducing Hidden Attractors in Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems Using Affine Transformations
This article proposes a unified approach for hidden attractors control in fractional-order chaotic systems. Hidden attractors have small basins of attractions and are very sensitive to initial conditions and parameters. That is, they can be easily drifted from chaotic behavior into another type of dynamics, which is not suitable for encryption applications that require quite wide initial conditions and parameters ranges for encryption key design. Hence, a systematic coordinate affine transformation framework is utilized to construct transformed systems with self-reproducing attractors
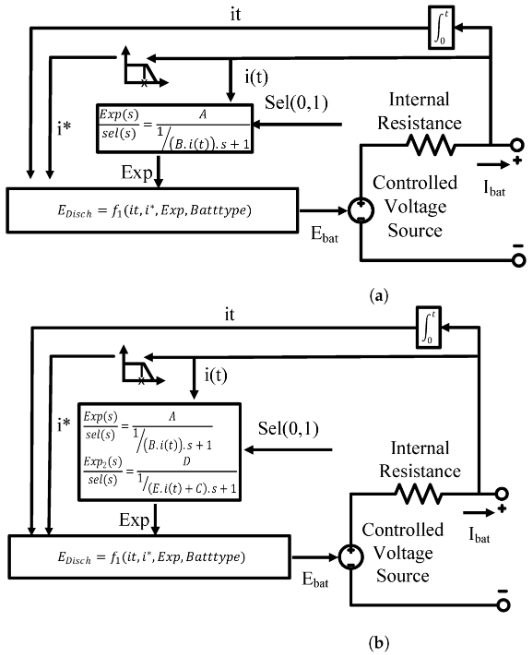
Parameter Identification of Li-ion Batteries: A Comparative Study
Lithium-ion batteries are crucial building stones in many applications. Therefore, modeling their behavior has become necessary in numerous fields, including heavyweight ones such as electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, as well as lightweight ones like sensors and actuators. Generic models are in great demand for modeling the current change over time in real-time applications. This paper proposes seven dynamic models to simulate the behavior of lithium-ion batteries discharging. This was achieved using NASA room temperature random walk discharging datasets. The efficacy of

Microstrip Coupled Line Bandpass Filter: A Stochastic Model
Coupled line microstrip filter is regarded to be a strong contender for high frequency and wireless applications, due to its compact size, inexpensive cost, and simple engineering manufacturing. The stochastic study of the proposed microstrip filter, based on the Monte Carlo Model, presented in this paper explores the uncertainties in the microstrip filter's design parameters and their influence on the filter's functionality. The filter's microstrip thickness, lengths, and spacing are all considered as design factors. The analysis investigates the variation of the standard deviations, the mean
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 17
- Next page ››
