Breadcrumb

Novel Edge AI with Power-Efficient Re-configurable LP-MAC Processing Elements
Deep learning has become increasingly important in various fields, such as robotics, image processing, and speech recognition. However, the high computational requirements of deep learning models make it challenging to deploy them on edge & embedded devices with constrained power and area budgets. This paper proposes a novel low-power technique for implementing deep learning models on edge devices called LP-MAC (Low Power Multiply Accumulate). LP-MAC is designed for fixed-point format operations and takes advantage of reusing the input vector for MAC operations. It provides a new hardware
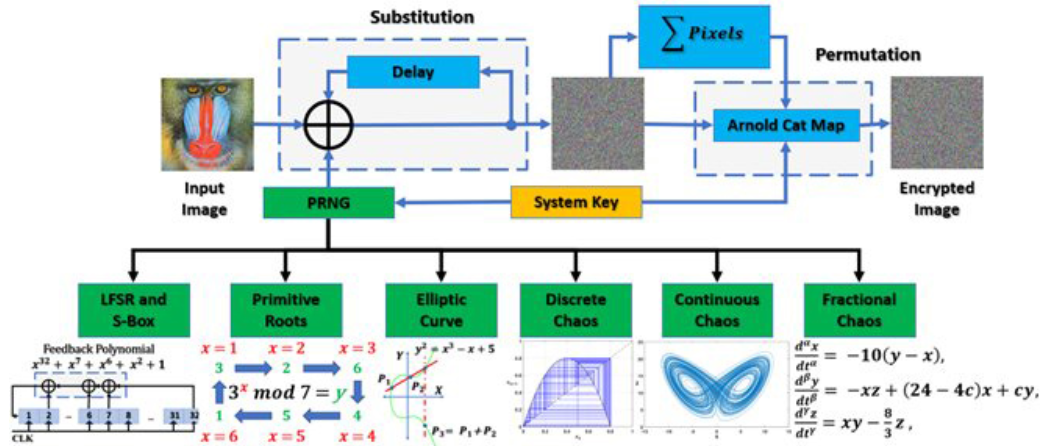
Analysis and Guidelines for Different Designs of Pseudo Random Number Generators
The design of an efficient Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) with good randomness properties is an important research topic because it is a core component in many applications. Based on an extensive study of most PRNGs in the past few decades, this paper categorizes six distinct design scenarios under two primary groups: non-chaotic and chaotic generators. The non-chaotic group comprises Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSR) with S-Boxes, primitive roots, and elliptic curves, whereas the chaotic group encompasses discrete, continuous, and fractional-order chaotic generators. This paper
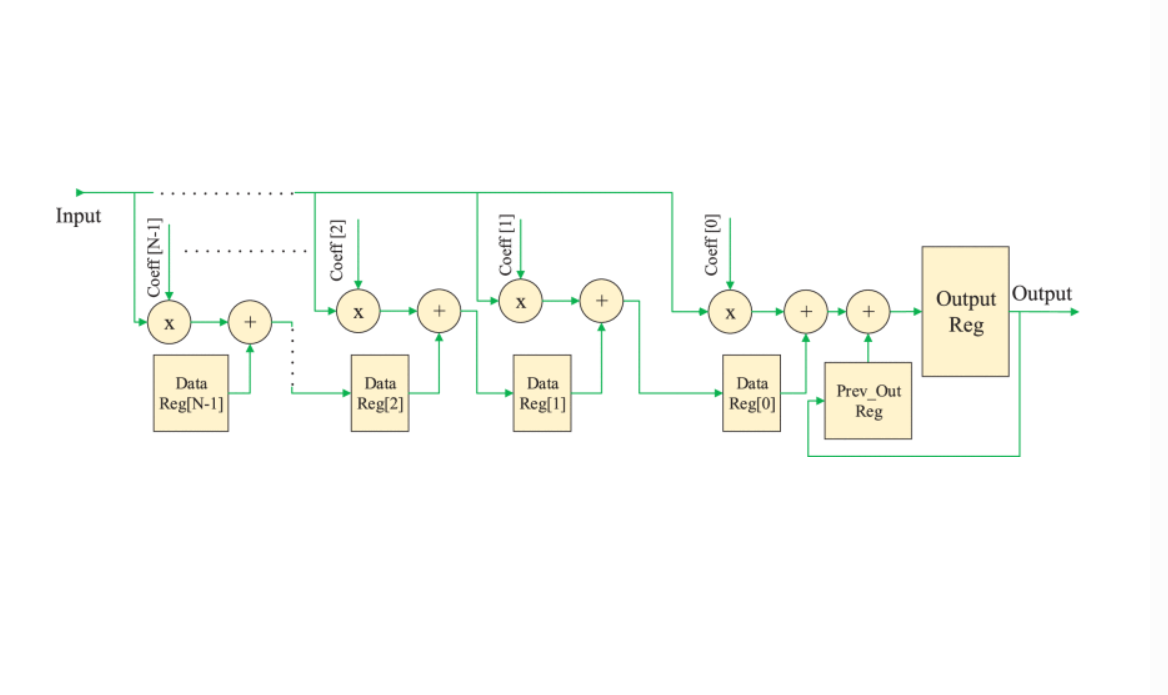
Hardware Accelerator of Fractional-Order Operator Based on Phase Optimized Filters With Applications
Hardware accelerators outperform CPUs in terms of performance by parallelizing the algorithm architecture and using the device’s programmable resources. FPGA is a type of hardware accelerator that excels not only in performance but also in energy efficiency. So, it provides a suitable platform for implementing complicated fractional-order systems. This paper proposes a novel phase-based optimization method to implement fractional operators using FIR and IIR filters. We also compare five fractional operator implementation methods on FPGA regarding resource utilization, execution time, power
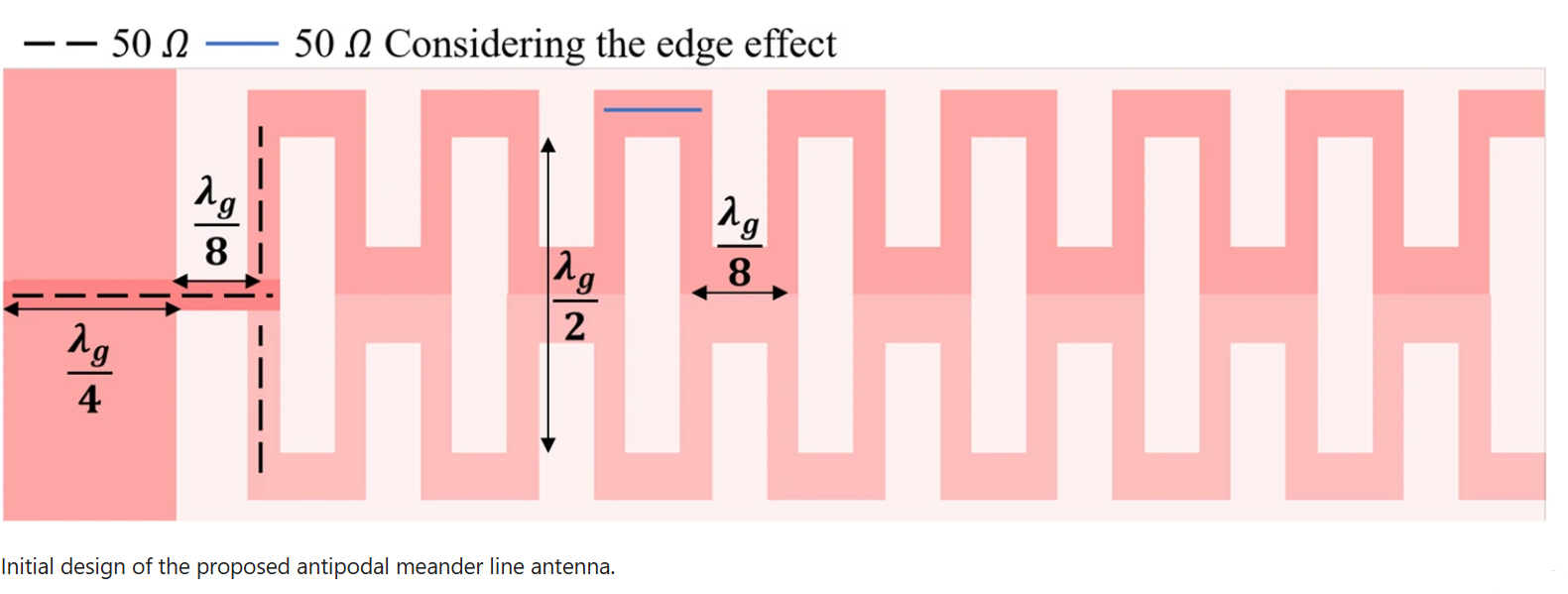
High gain antipodal meander line antenna for point-to-point WLAN/WiMAX applications
This paper introduces a planar antipodal meander line antenna fabricated using RO3003 substrate. The proposed antenna is designed to radiate in the end-fire direction, achieving a maximum measured gain of 10.43 dBi within its working bandwidth, which ranges from 2.24 GHz to 2.7 GHz, covering long-range WLAN/WiMAX applications. A systematic procedure is adopted in the design process to prove its tunability to cover other application requirements in terms of gain and bandwidth. The proposed design steps show that the bandwidth and the gain can independently be controlled by adjusting specific
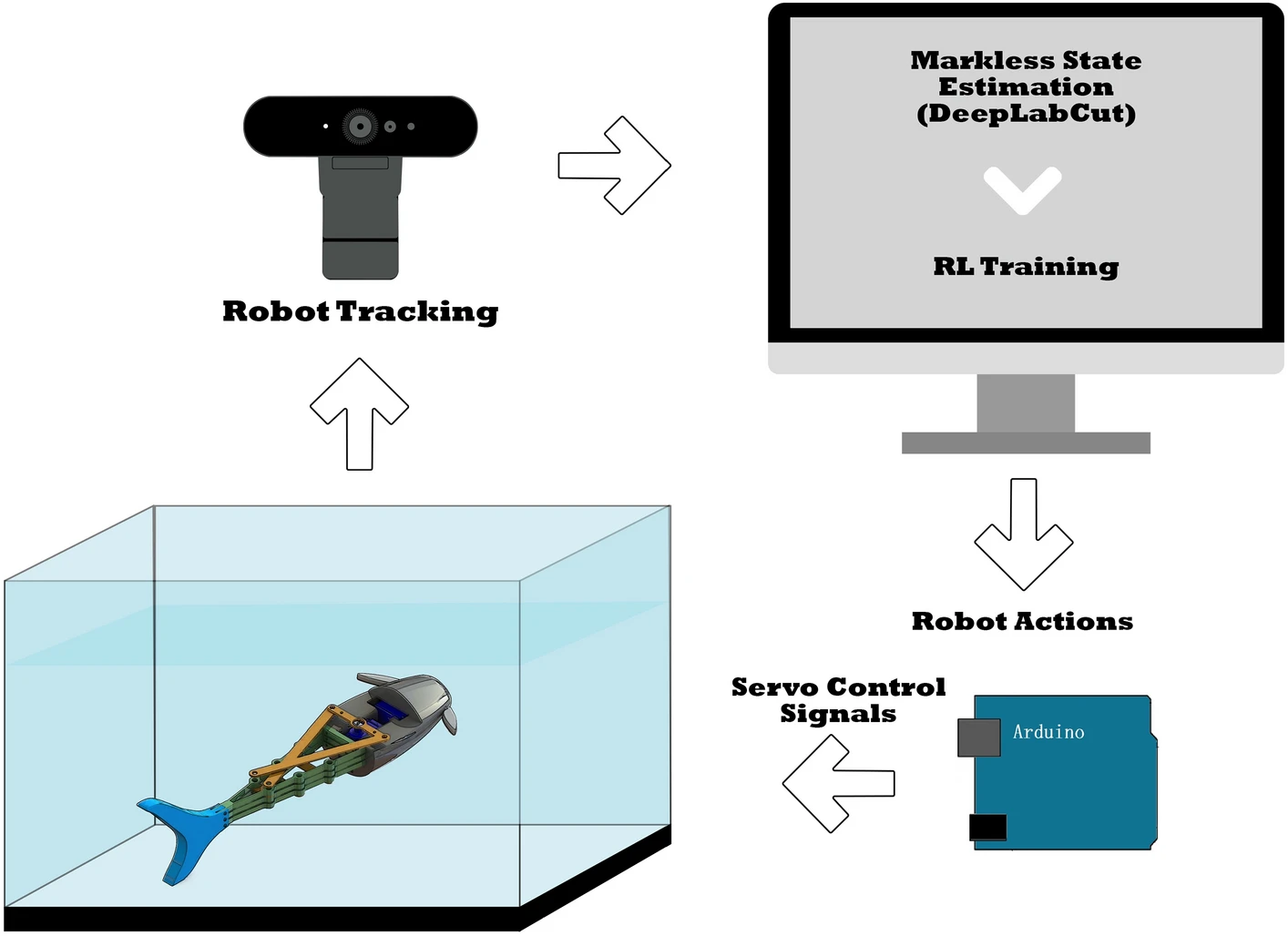
Design and control of soft biomimetic pangasius fish robot using fin ray effect and reinforcement learning
Soft robots provide a pathway to accurately mimic biological creatures and be integrated into their environment with minimal invasion or disruption to their ecosystem. These robots made from soft deforming materials possess structural properties and behaviors similar to the bodies and organs of living creatures. However, they are difficult to develop in terms of integrated actuation and sensing, accurate modeling, and precise control. This article presents a soft-rigid hybrid robotic fish inspired by the Pangasius fish. The robot employs a flexible fin ray tail structure driven by a servo
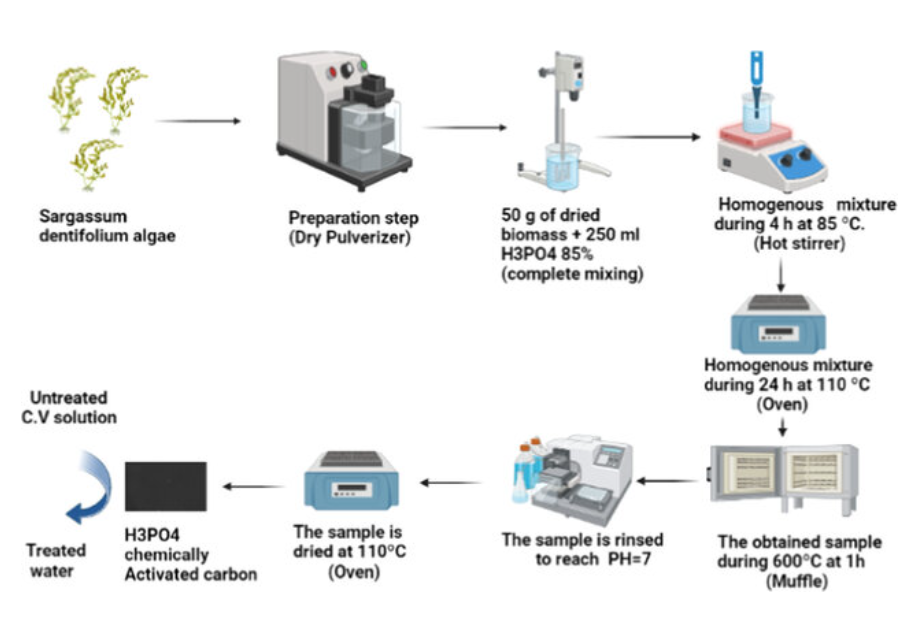
Crystal violet removal using algae-based activated carbon and its composites with bimetallic Fe0-Cu
The textile industry is considered a source of pollution because of the discharge of dye wastewater. The dye wastewater effluent has a significant impact on the aquatic environment. According to the World Bank, textile dyeing, and treatment contribute 17 to 20% of the pollution of water. This paper aims to prepare the bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0-Cu), algae-activated carbon, and their composites (AC-Fe0-Cu), which are employed as adsorbents. In this paper, Synthetic adsorbents are prepared and examined for the adsorption and removal of soluble cationic crystal violet (CV) dye
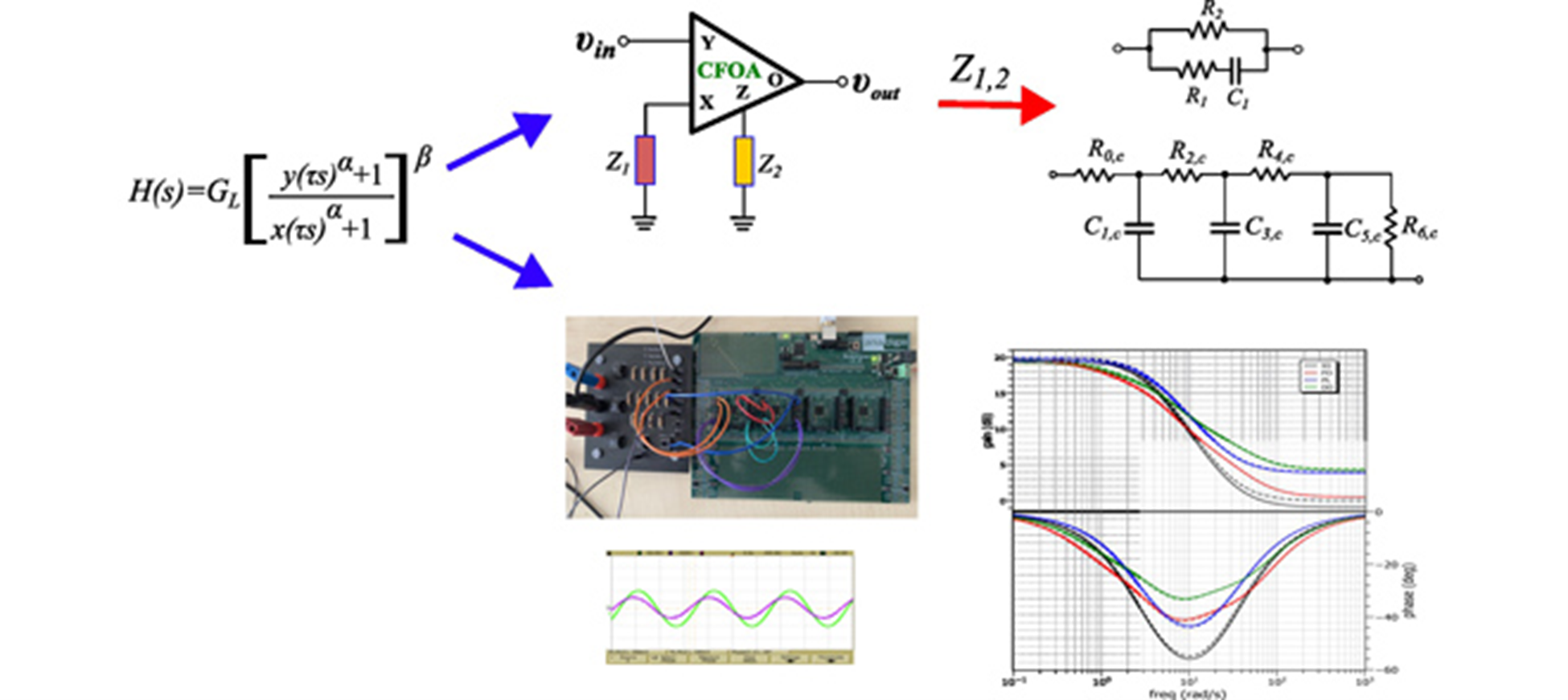
Bilinear Double-Order Filter Designs and Application Examples
A novel kind of non-integer order bilinear filters, named double-order bilinear filters, is introduced in this work. They are based on the employment of two non-integer orders, offering the maximum design flexibility in comparison with their fractional-order and power-law counterparts. An attractive offered benefit is that this is achieved without increasing the circuit complexity, since the proposed structure is capable of realizing all non-integer kinds of filters. Two design examples are provided, where it is shown that lead/lag compensators utilized in control applications and low/high
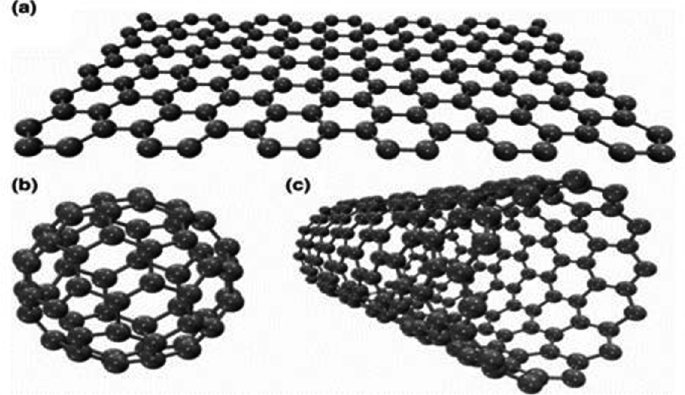
Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Composites as Adsorbents
Carbon nanomaterials with various nanostructures (carbon nanotubes, graphene, graphene oxide, fullerene, nano diamonds, carbon quantum dots, carbon nanofibers, graphitic carbon nitrides, and nano porous carbons) are the decade’s most distinguishing and popular materials. They have distinctive physicochemical qualities such as chemical stability, mechanical strength, hardness, thermal and electrical conductivities, and so on. Furthermore, they are easily surface functionalized and tweaked, modifying them for high-end specific applications. Carbon nanostructures’ properties and surface
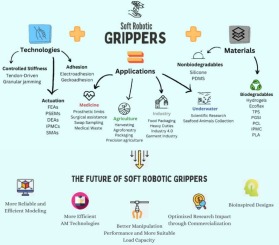
Soft robotic grippers: A review on technologies, materials, and applications
The growing need for manipulators capable of handling delicate objects with care and coexisting safely with humans has brought soft robots to the forefront as a practical and cost-effective solution. In this context, this paper aims to explore soft grippers, a unique and versatile subset of soft robots. It provides an overview of various soft grasping techniques and materials, highlighting their respective advantages and limitations, along with showcasing several designed and tested models. As medicine and agriculture are acknowledged as pivotal domains required for basic human survival, this

Review on Coral Reef Regeneration Methods through Renewable Powered Electrotherapy
The restoration of coral reef population in coastal regions is currently a growing concern. Many attempts have been made to apply new approaches to limit the deterioration of coral reefs, and to accelerate the growth of new reefs to protect coastal areas and ecosystems using available renewable energy sources. This paper highlights the new approaches and their various advantages and limitations in tidal and wave energy. The paper also suggests improvements to some of those systems using the recent developments in soft robotics, especially the use of biomimetic fish as a feasible support
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
