Breadcrumb

Memristive Fractional-Order Nonlinear Model for Circuit Design
The main objective of this chapter is to bring together studies addressing the current research and history of memristive device evolution available in the literature. The chapter highlights the methodologies and frameworks relevant to the development of nonlinear memristor models suitable for future nanoscale circuit design. An elaborate study of memristor device physics, structure, operation, mathematical modeling, and TCAD simulations is carried out for better understanding of nonlinear models of memristive devices. The memristive device features and content related to memristor nonlinear
Di- and tri- cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal using different prepared materials based Sargassum dentifolium algae, and iron oxide
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are highly toxic and carcinogenic compounds as they are low water solubility, hardly degradable and may persist in the environment for many years. Therefore, this study was directed to PAHs ‘anthracene and naphthalene’ removal using a combination method between adsorption and degradation using sunlight. Three adsorbent materials, iron oxide (Fe) alone, Sargassum dentifolium (S) alone, and mixture of Iron oxide and Sargassum dentifolium (FeS) were prepared. Afterwards, optimisation process was performed for the three adsorbent forms through some
Time-Frequency Design of a Multi-Sine Excitation with Random Phase and Controllable Amplitude for (Bio) Impedance Measurements
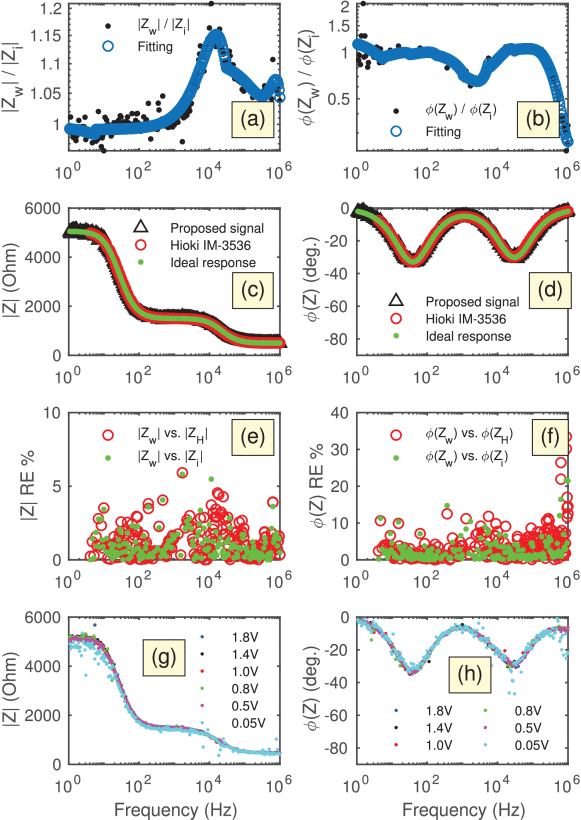
Impedance spectroscopy has become a standard electroanalytical technique to study (bio)electrochemical and physiological systems. From an instrumentation point of view, the measurement of impedance can be carried out either in the frequency domain using the classical frequency sweep method or in the time domain using a variety of broadband signals. While time-domain techniques can be implemented with relatively simple hardware and can achieve faster acquisition time, they are still not that popular because of their lower accuracy and modularity. In this work we present a method and an

A collection of interdisciplinary applications of fractional-order circuits
An attractive feature of fractional calculus is its application in various interdisciplinary fields, extending from biomedical and biological notions to mechanical properties. For their description, fractional-order models have outperformed the corresponding integer-order models, resulting in a more realistic behavior, due to the additional degrees of freedom offered and the long-term memory effect that reflects the fractional order. These improved features are processed by appropriate circuit implementations, derived through several approximation methods, whose primary objective is to provide
Fractional-Order Filter Design
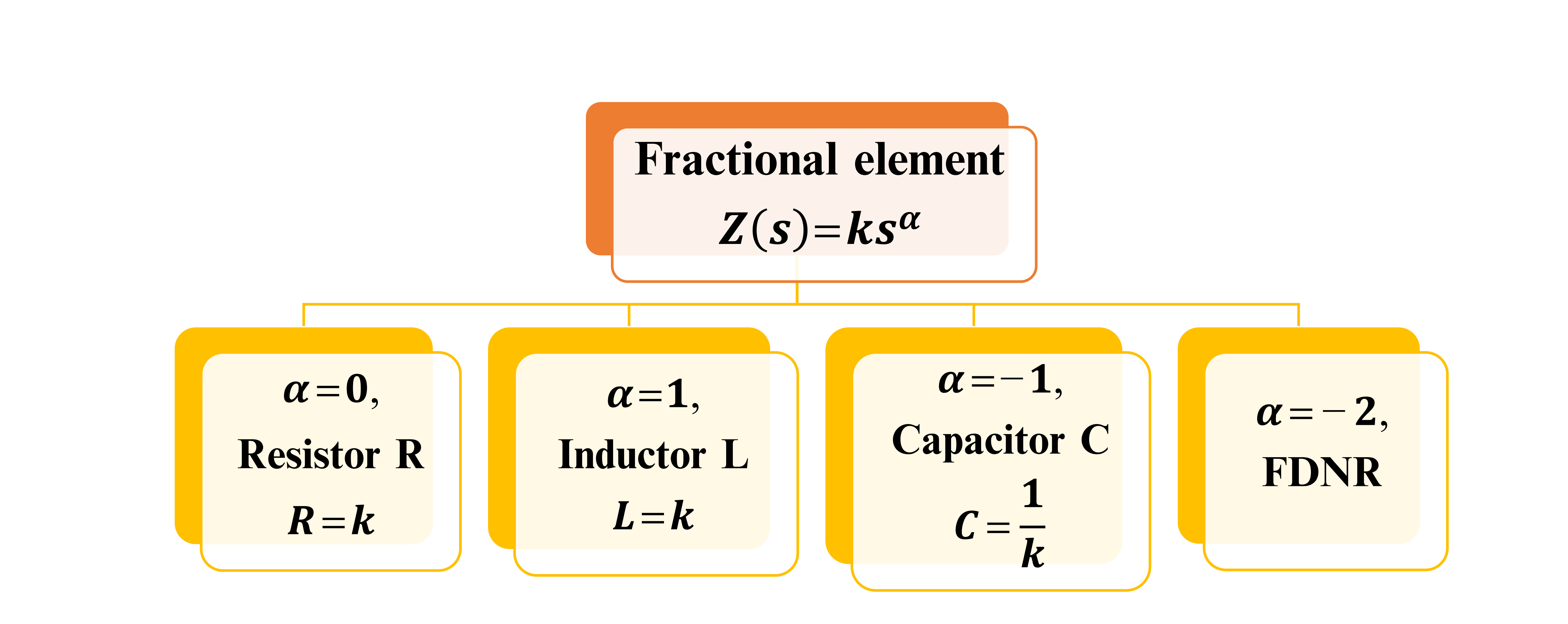
One of the advantages of fractional order is the extra degree of freedom added by the fractional-order parameters, which enrich the analysis with more details in new dimensions. This chapter introduces factional-order conventional filters of orders α, 2α, and 3α. The general transfer functions of continuous-time filters (low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters) to the noninteger-order (fractional-order) domain are investigated. Also, mathematical expressions for the maximum and minimum frequencies, the half power frequencies, and the right-phase frequencies are derived. In addition, the
Tikhonov regularization for the deconvolution of capacitance from the voltage–charge response of electrochemical capacitors
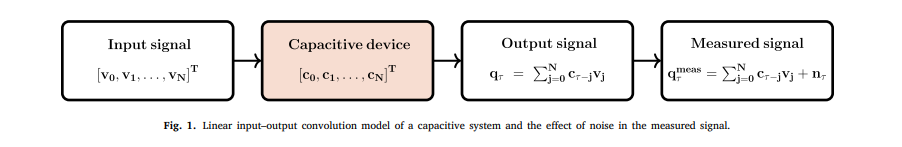
The capacitance of capacitive energy storage devices cannot be directly measured, but can be estimated from the applied input and measured output signals expressed in the time or frequency domains. Here the time-domain voltage–charge relationship of non-ideal electrochemical capacitors is treated as an ill-conditioned convolution integral equation where the unknown capacitance kernel function is to be found. This comes from assuming a priori that in the frequency domain the charge is equal to the product of capacitance by voltage, which is in line with the definition of electrical impedance

Synthesis of resonance-based common-gate fully differential band-pass filters
We propose a class of fully differential filters based on a common-gate differential amplifier cell in three different topologies. Our focus is on the synthesis of second-order band-pass filters and we found 53 possible circuits. All filters are resonance-based and have electronically tunable gain. Post layout simulations in 65-nm CMOS technology are provided to validate the proper function of these filters. © 2022 Elsevier B.V.
Field Programmable Analog Array Based Non-Integer Filter Designs
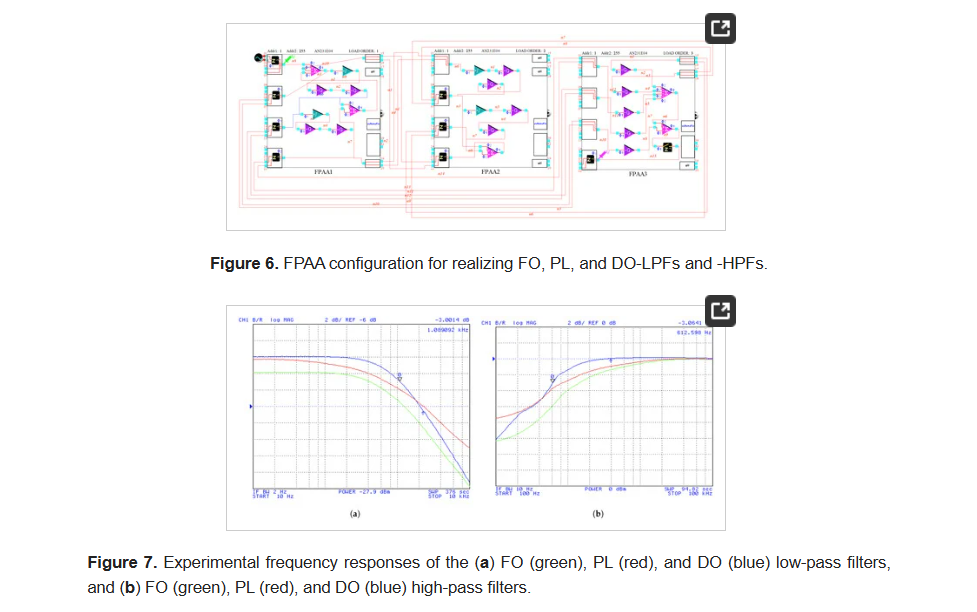
The approximation of the frequency behavior of fractional-order, power-law, and double-order filters can be performed by the same rational integer-order transfer function. This can be achieved through the utilization of a curve fitting based approximation. Moreover, their implementation can be performed by the same core, by only changing the corresponding time constants and scaling factors. The aforementioned findings are experimentally verified using a Field Programmable Analog Array device. © 2023 by the authors.
Robust adaptive supervisory fractional order controller for optimal energy management in wind turbine with battery storage
To address the challenges of poor grid stability, intermittency of wind speed, lack of decision-making, and low economic benefits, many countries have set strict grid codes that wind power generators must accomplish. One of the major factors that can increase the efficiency of wind turbines (WTs) is the simultaneous control of the different parts in several operating area. A high performance controller can significantly increase the amount and quality of energy that can be captured from wind. The main problem associated with control design in wind generator is the presence of asymmetric in the
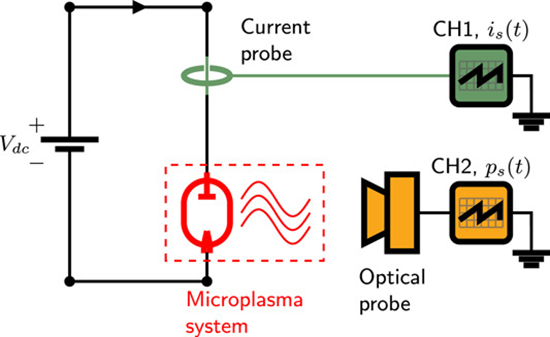
Parallel random bitstreams from a single source of entropy based on nonthermal electrochemical microplasma
This study presents the simultaneous generation of two uncorrelated and continuous high-quality random bitstreams originating from a single physical system based on confined, nonthermal electrochemical microplasma operating under atmospheric conditions. The randomness is intrinsically inherited from the time-resolved electrical current and optical emission intensities of the microplasma system, which were collected using wide bandwidth current probe and photodetection device. The parallel bitstreams pass unambiguously all 15 NIST SP 800-22 statistical tests without the need for any data post
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
