Breadcrumb
A computational flow model of oxygen transport in the retinal network
The retina's high oxygen demands and the retinal vasculature's relatively sparse nature are assumed to contribute to the retina's specific vulnerability to vascular diseases. This study has been designed to model the oxygen transport in physiologically realistic retinal networks. A computational fluid dynamics study has been conducted to investigate the effect of topological changes on the oxygen partial pressure distribution in retinal blood vessels. The Navier Stokes equations for blood flow and the mass transport equation for oxygen have been coupled and solved simultaneously for the
Review and novel contributions to amplifier-based oscillator design
This paper reviews amplifier-based oscillator topologies and introduces new ones while reporting all possible circuits that can be obtained from some of them using exhaustive searching. Second-order as well as third-order RC and RLC oscillators are reported and selected circuits are designed and experimentally verified. Incorporating non-ideal and nonlinear effects into the modeling of these amplifier-based oscillators are demonstrated. © 2024
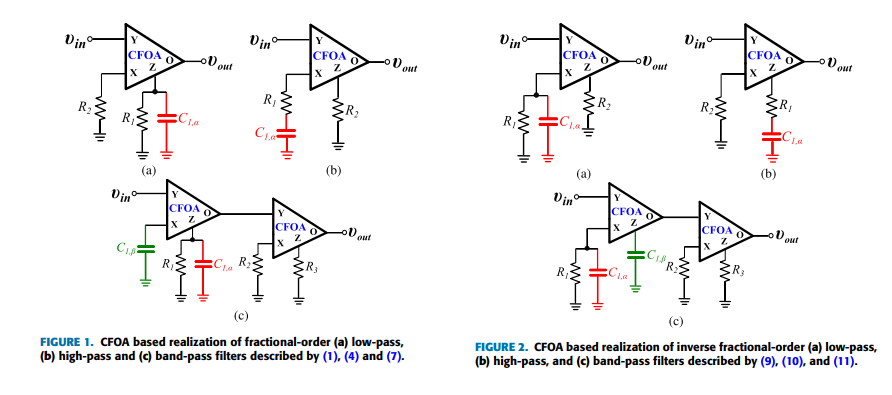
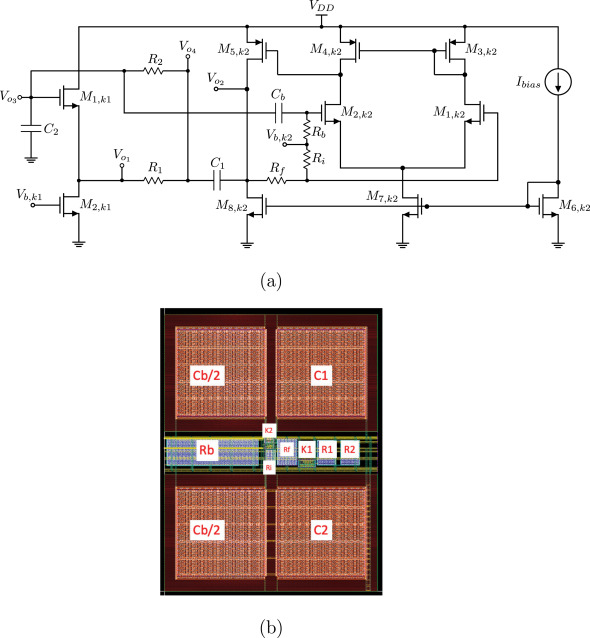
Non-Integer Order Generalized Filters Designs
Non-integer order filters can be derived from a generalized structure presented in this work. More specifically, fractional-order and power-law filters of single- or double-order are special cases of non-integer order filters with three degrees of freedom and can be implemented using a Current Feedback Operational Amplifier as the active element. The transfer function is formed as a ratio of two impedances which can be synthesized using Foster or Cauer RC networks. A curve-fitting based technique is employed for approximating the magnitude and phase of each impedance. The behavior of the
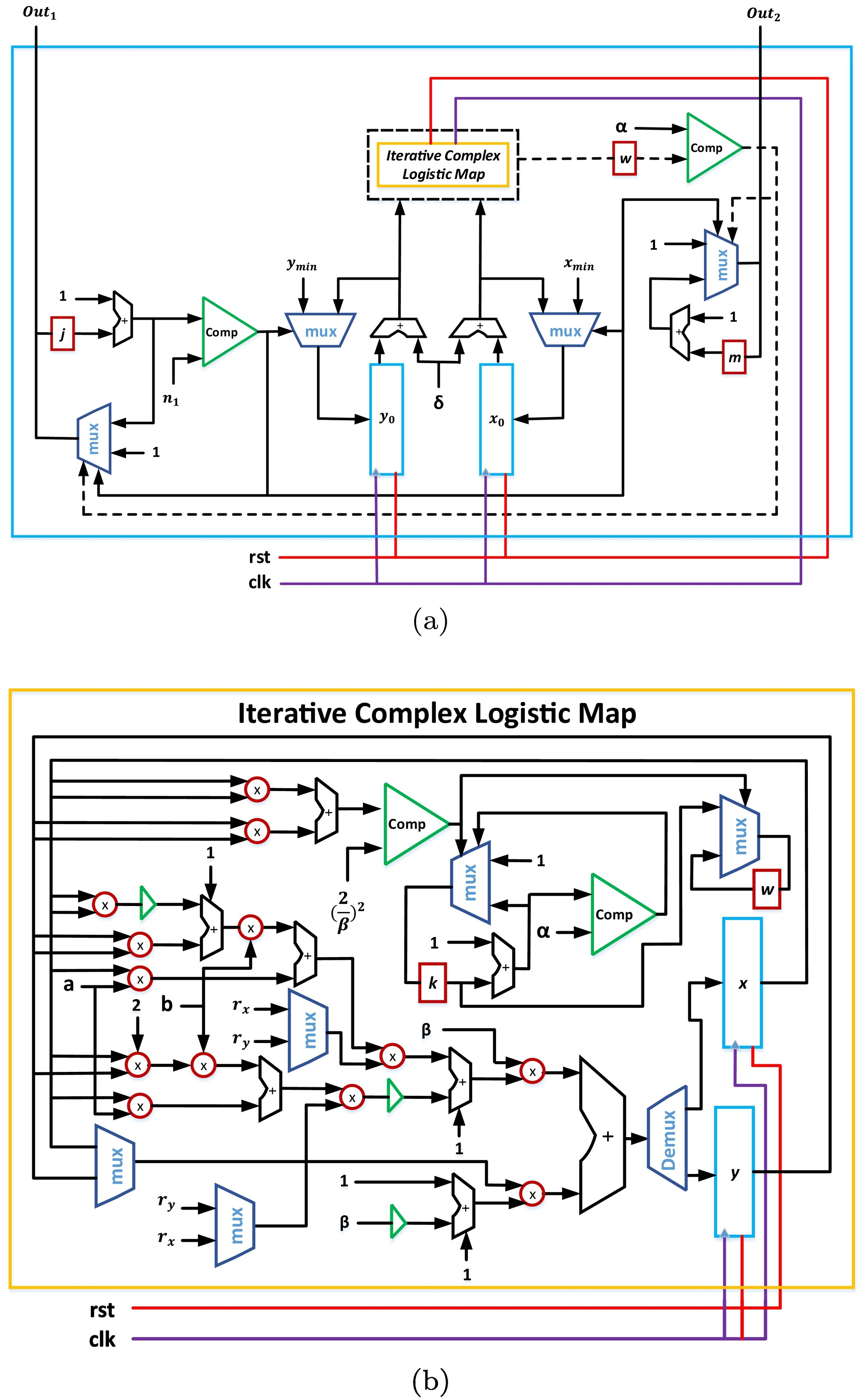
FPGA realization of fractals based on a new generalized complex logistic map
This paper introduces a new generalized complex logistic map and the FPGA realization of a corresponding fractal generation application. The chaotic properties of the proposed map are studied through the stability conditions, bifurcation behavior and maximum Lyapunov exponent (MLE). A relation between the mathematical analysis and fractal behavior is demonstrated, which enables formulating the fractal limits. A compact fractal generation process is presented, which results in designing and implementing an optimized hardware architecture. An efficient FPGA implementation of the fractal behavior
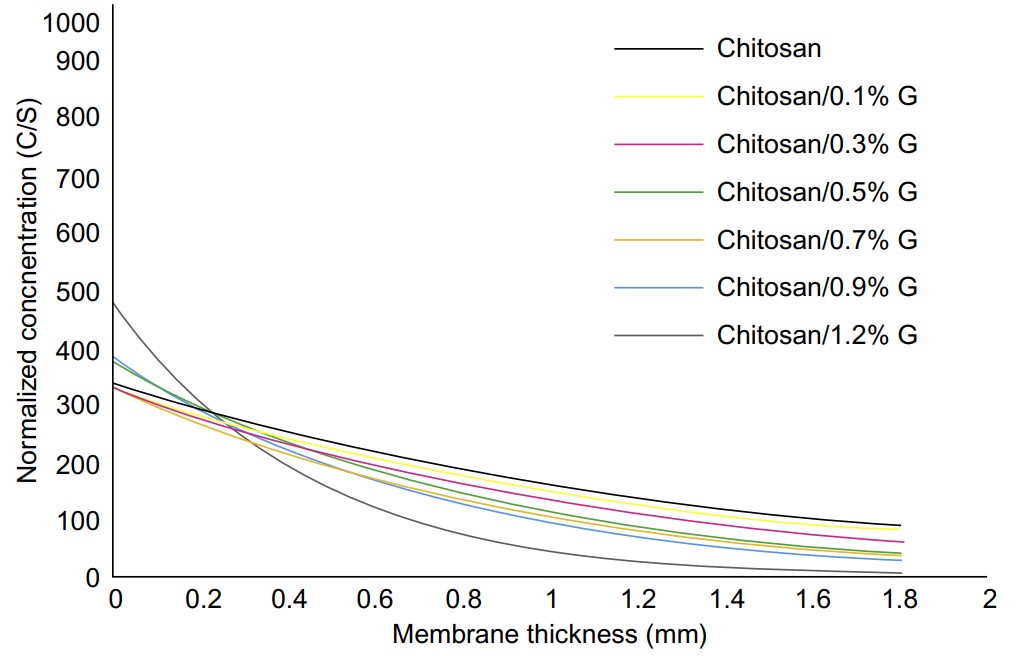
Design and fabrication of CNT/graphene-based polymer nanocomposite applications in nanosensors
Development and improvement of nanosensors have been active research areas over the last few decades. Many materials and compounds have been investigated for their sensing properties. This work is concerned with developing a new sensing layer for gas sensors based on chitosan as a polymer enhanced with graphene as a nanofiller. The graphene used for preparing the chitosan solution was at 0.1, 0.5, and 1 wt%. Many characterizations (such as using different pore size, gas permeability, mechanical properties, and electrical resistance) were tested to give full insight into the nanocomposite
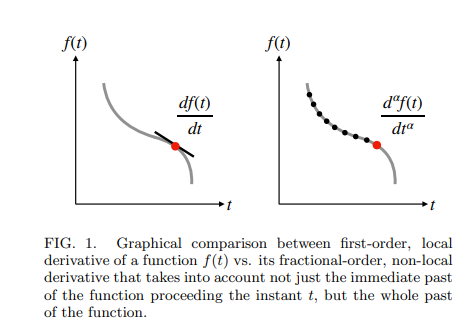
Extended RC Impedance and Relaxation Models for Dissipative Electrochemical Capacitors
Electrochemical capacitors are a class of energy devices in which complex mechanisms of accumulation and dissipation of electric energy take place when connected to a charging or discharging power system. Reliably modeling their frequency-domain and time-domain behaviors is crucial for their proper design and integration in engineering applications, knowing that electrochemical capacitors in general exhibit anomalous tendency that cannot be adequately captured with the traditional RC-based models. In this study, we first review some of the widely used fractional-order models for the
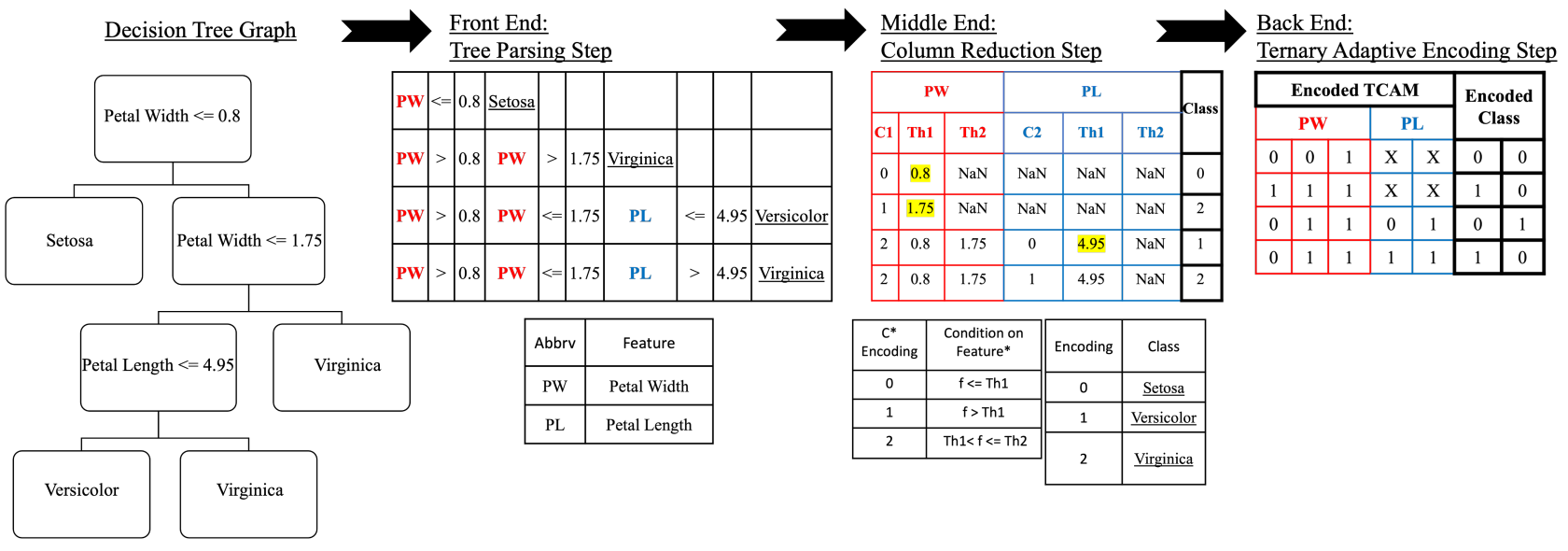
DT2CAM: A Decision Tree to Content Addressable Memory Framework
Decision trees are powerful tools for data classification. Accelerating the decision tree search is crucial for on-the-edge applications with limited power and latency budget. In this article, we propose a content-addressable memory compiler for decision tree inference acceleration. We propose a novel 'adaptive-precision' scheme that results in a compact implementation and enables an efficient bijective mapping to ternary content addressable memories while maintaining high inference accuracies. We also develop a resistive-based functional synthesizer to map the decision tree to resistive
Deep Learning Based Kinematic Modeling of 3-RRR Parallel Manipulator
This paper presents a novel low cost design for a 3-RRR Planar Parallel Manipulator (PPM). These manipulators proved their superiority over serial manipulators due to their speed, precision and smaller work space where the work space area is accounted for in the design to ensure that the robot is performing its task in a smooth and simple way without getting into any singularity points. The challenge with PPM is to obtain the kinematic constraint equations of the manipulator due to their complex non-linear behavior. Screw theory is a new approach that is used to compute the direct and inverse

Commercial Versus Natural Activated Carbon Fabricated Sheets: Applied to Dyes Removal Application
Industrial dyes are considered one of the main causes of increased water pollution of water. Many businesses, such as steel and paper, are located along riverbanks because they require large amounts of water in their manufacturing processes, and their wastes, which contain acids, alkalis, dyes, and other chemicals, are dumped and poured into rivers as effluents. For example, chemical enterprises producing aluminum emit a significant quantity of fluoride into the air and effluents into water bodies. Fertilizer facilities produce a lot of ammonia, whereas steel plants produce cyanide. Many
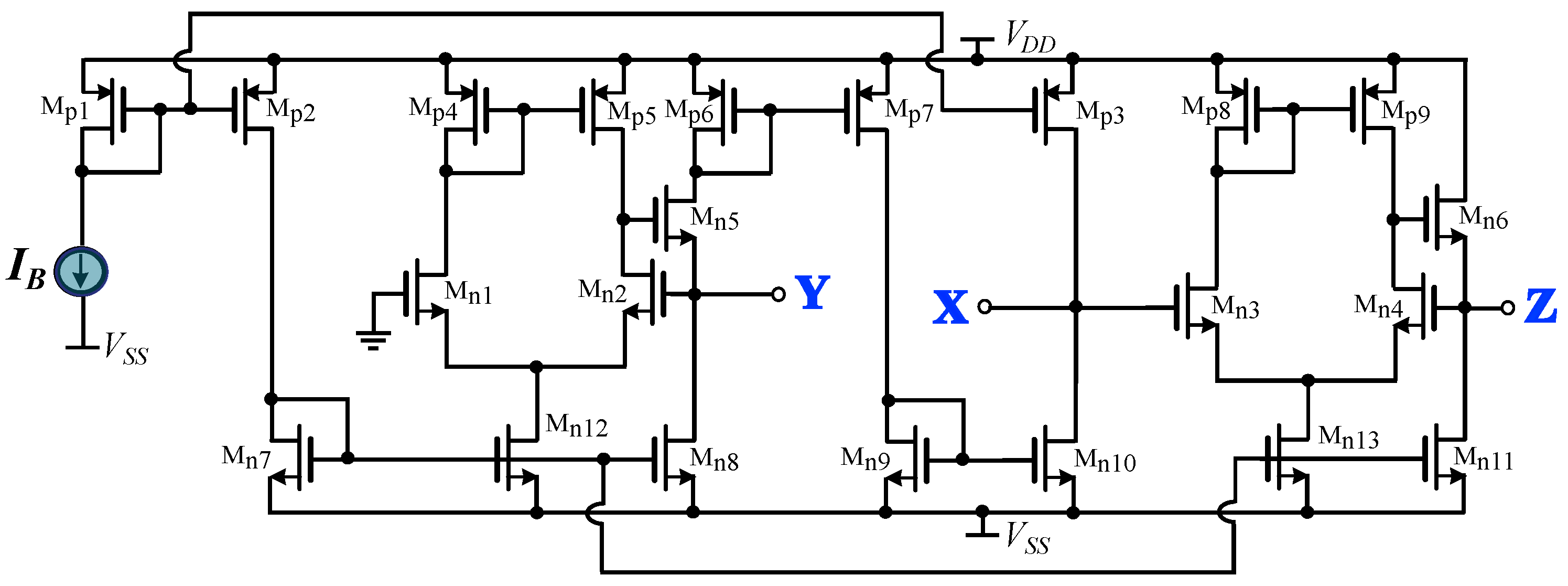
Minimum Active Component Count Design of a PIλDμ Controller and Its Application in a Cardiac Pacemaker System †
A generalized structure for implementing fractional-order controllers is introduced in this paper. This is achieved thanks to the consideration of the controller transfer function as a ratio of integer and non-integer impedances. The non-integer order impedance is implemented using RC networks, such as the Foster and Cauer networks. The main offered benefit, with regards to the corresponding convectional implementations, is the reduced active and, also, passive component count. To demonstrate the versatility of the proposed concept, a controller suitable for implementing a cardiac pacemaker
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
